Novel Approaches in Drug Designing & Development - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
Prevalence of malaria during pregnancy and the spate of drug resistance by malaria parasites have constantly impacted maternal, perinatal and neonatal outcomes, especially in sub-Saharan Africa. Inhibiting binding; or displacement of bound infected erythrocytes from the placenta as an adjunct treatment or vaccine for malaria was considered an option towards ending pregnancy associated malaria in this study. Molecular modeling and toxicity predictors used in this study indicated that among the ligands screened, IH3 had the lowest binding energy of -9.8Kcal/mol while var2csA had -2.8Kcal/mol. Var2csA is parasite’s adhesive protein. It was also observed that out of the 90 ligands (binding affinity range -9.8 to -1.0 Kcal/mol) screened, IH3 (-9.8Kcal/mol), FAD (-8.4 Kcal/mol), NDP (-8.2 Kcal/mol), A5A (-8.2 Kcal/mol), ABO (-8.1 Kcal/mol), IH2 (-7.8 Kcal/mol), 2RT (-7.7 Kcal/mol), CRO (-7.7 Kcal/mol) and IH1 (-7.7 Kcal/mol) appear to be the most promising lead compounds to occupy var2csA binding pocket in pCSA in order to prevent adhesion of malaria infected erythrocytes to the placenta. SwissADME and Molinspiration Cheminformatics for LogP (mean of 1.07 and range of -2.79 to 4.18) of the lead compounds showed no correlations between lipophilicity and interaction with receptors. Of all the compounds selected for analysis, only ABO and 2RT exhibited drug-like properties based on Ghose, Lipinski and Veber filters. The data therefore suggests that IH3, FAD, NDP, A5A, ABO, IH2, 2RT, CRO, IH1 and var2csA make favourable lead candidates for targeting pCSA and therefore require further in vitro and in vivo evaluations.
Keywords: Malaria; Pregnancy; Modeling; Toxicity; Auto Dock
Abbreviations: pRBCs: Parasitized Red Blood Cells; IEs: Infected Erythrocytes; DC: Domain Cassette; EPCR: Endothelial Protein C Receptors, PAM: Pregnancy Associated Malaria; DARC: Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines; EC: Endothelial Cell; IPT: Intermittent Preventive Treatment; PDB: Protein Data Bank; TEST: Toxicity Estimation Software Tool; FAD: Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
Introduction
Background to the Study
Malaria is one of the leading causes of death in tropical, underdeveloped countries throughout the world. Malaria in pregnancy is a major global public health concern; this has been attributed to transient depression in cell-mediated immunity which has increased the susceptibility of pregnant women to malaria and its adverse outcomes. Approximately 32.3% of pregnant women in sub-Saharan Africa are at the risk of malaria yearly [1]. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium sp transmitted by the bite of the female Anopheline mosquito. Upon infection, the life cycle of the Plasmodium sp. begins and ends in the bloodstream where erythrocytes are infected and consequently destroyed, causing symptoms such as anemia, respiratory sequelae, cerebral malaria, metabolic acidosis, and eventually organ failure, leading to death [2]. However, before the total destruction of erythrocytes occurs, there seems to be a mode by which the parasitized red blood cells (pRBCs) become sequestered or adhered in particular sites throughout the vascular system [3] and this results in widespread sequestration of infected erythrocytes (IEs) and hence their reduced clearance from the blood stream by the spleen [4]. Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) mediates this adhesion of IEs to various host receptors on the vascular lining during the blood stage of malaria infection [4-6].
Proteins of the PfEMP1which include var2csA (DBL2x, DBL3x and DBL6ɛ), Var1csa (DBL3γ), CIDR groups B & C, CIDR of DC8 group A, CIDR of DC13, DC4, DC8, DC5, Duffy Binding Protein (DBP) for Pv & Pk, and PfRh4 for Pf, PfRh5, EBA - 175, EBL -1, EBA - 140 and EBA 181 mediate adhesion and cell invasion through specific binding to multiple endothelial cell (EC) receptors, including domain cassette (DC) 36, DC31also known as platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM -1) or cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) [7], DC13, DC8, intercellular adhesion molecule -1 (ICAM - 1), E-selectin, endothelial protein C receptors (EPCR), duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC), and placental chondroitin sulfate A (pCSA). Others include: CD36, complement receptor - 1 also known as CD35 (i.e.; C3b, or C4b), VLA-4, LW, CD 58, CD 147, CD44, B-CAM/LU and Glycophorin A (F actin and G actin).
In this study, we focused on pregnancy associated malaria (PAM) also referred to as placental malaria (PM) which is mediated by Plasmodium falciparum elaborated var2csA that binds to placental chondroitin sulfate A (pCSA) to bring about sequestration of malaria IEs on the placental cyncytiotrophoblast. Each Plasmodium falciparum parasite genome constitutes over 59% var genes [5,8] and individual parasite expresses a single var gene at a time [9], maintaining all other var genes in a transcriptionally silent state. Almost all members of the var family are classified into one of 3 major groups (A, B, and C) based on a combination of chromosomal location, transcription direction, and upstream promoter sequence [10]. As an important activity in many drug discoveries projects, in silico molecular modeling was employed to identify molecules with activity against pCSA and subsequent lead optimization of the hits identified [11].
Statement of the Problem
Use of insecticide treated net and intermittent preventive treatment (IPT) are currently the preventive strategies to improve maternal and fetal outcomes amidst the ravaging malaria scourge. However, due to waning efficacy of the IPTs and insecticide treated nets as a result of resistant strains of the parasite and the malaria transmitting vectors, these preventive measures have become ineffective and less reliable over-time. This problem has persisted for a while now and there is no valid vaccine yet to prevent malaria, especially, placental malaria [12].
In this study, our target is to identify ‘‘in silico”, for the purpose of clinical application, non-recombinant product(s) that can competitively inhibit Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes (PfIEs) form binding, or displace bound PfIEs from placental chondroitin sulfate A since no antibody or antigen based vaccine tend to be successful in the search for vaccine against pregnancy associated malaria.
Aim and Objectives of the Study
Aim
This study aims to discover “in silico” non recombinant molecules which can interact with placental chondroitin sulfate to inhibit binding or displace bound var2csA from the placenta in order to prevent pregnancy associated malaria.
Objectives
1. To generate a library of molecules similar to var2csA (ligands to CSA) from available databases.
2. Dock these molecules against placental CSA in order to generate hits with favorable binding affinity with it; and
3. Analyze “in silico” the suitability and safety of some of the selected molecules as drugs.
Operational Definition of Terms
1. Autodock: Molecular modeling simulation software. It is especially effective for protein–ligand docking.
2. Binding affinity: The strength of the binding interaction between a single biomolecule to its ligands.
3. Databases: A collection of information that is organized so that it can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. Example here include PDB and PubChem.
4. Virtual molecular screening (also known as molecular docking): A computational technique used in drug discovery to identify those structures which are most likely to bind a drug target, typically a protein or enzyme.
Literature Review
Concept of Drug Design and Receptor Interaction
Many micro and macroscopic properties of substance, such as biological activities of drugs and drug-like compounds are controlled by their stereochemistry. Molecules with one or more rotational degree of freedom (rotatable bonds) exhibit conformational isomerism, where the stable conformers correspond to energy minima, and therefore, to the most probable structures to be found in materials, pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals [13]. Interaction stabilizing conformations are provided by certain hydrogen bonding even though others also take place in many cases, as seen in electrostatic effects and hyperconjugation phenomena, i.e, electron donation from the endocyclic oxygen lone pair toward the vicinal axial antibonding orbital [14]. For example, the core of the CSA-binding site is situated in the N-terminal part of var2csA by hydrogen bonding and van der Waal force (Figure 1). The following equation [EI ]aq [E]aq +[I ]aq is used to determine the reaction involving a receptor and its ligand. The change in free energy of binding (ΔG) is related to binding affinity, ( ΔG = −RTInkA).

Where E = Receptor, I = Ligand, KA = Equilibrium constant, R = ideal gas constant = 8.314J/mol-K, and T = Temperature of the reaction (Kelvin).
Receptor and ligand docking aim at correct prediction of the structure of the complex under equilibrium conditions. The docking techniques used in this study included prediction of the binding modes of novel drugs (ligands) and the study of proteinprotein interactions using AutoDock Vina (http://vina.scripps. edu) tool in PyRx (http://pyrx.sourceforge.net) where autodock reproduces nine different protein - ligand complexes for which the structure of the macromolecule was known without prior knowledge of the binding site. The more negative the binding affinity becomes, (i.e, the lower the binding energy), the better the orientation of the ligand in the binding pocket of the receptor.
The autodock programme package - PyRx was able to select the correct complexes based on the energy without prior knowledge of the binding site; (i.e, blind docking). PyRx was not able to see the binding site but was able to find it.
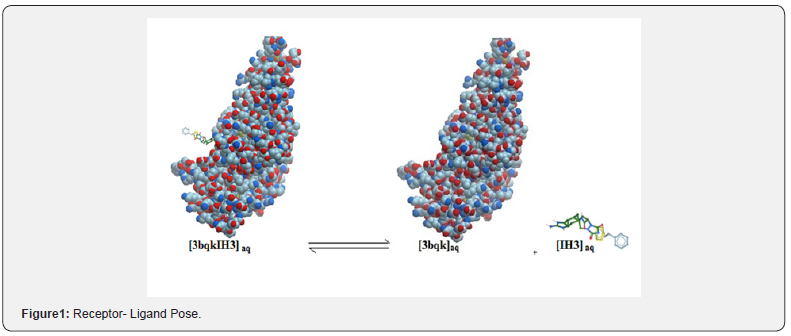
Prediction of correct structure (posing) of the [EI ] complex does not require information about kA. Prediction of biological activity (ranking) does require information about KA . For the complex [EI ] , the following factors are important: steric, electrostatic, hydrogen bonding inhibitor strain (if flexible) and enzyme (receptor) strain. Important factors when considering the equilibrium include: desolvation, rotational entropy, and translational entropy. Most scoring functions focus on energetic than entropic effects. The events of ligand-binding are driven by a combination of enthalpic and entropic effects, either of which can dominate specific interactions [15-17].
Var2csA
Var2csA is a variant of many adhesive proteins of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) elaborated on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes for the purpose of tethering infected cells on tissue receptors to evade destruction by the spleen. Var2csA protein consists of six DBL domains, a single transmembrane helix, cytopasmic acidic terminal sequence and significant interdomain regions (Figure 2). Four of the DBL domains have been shown to bind CSA [18-20].
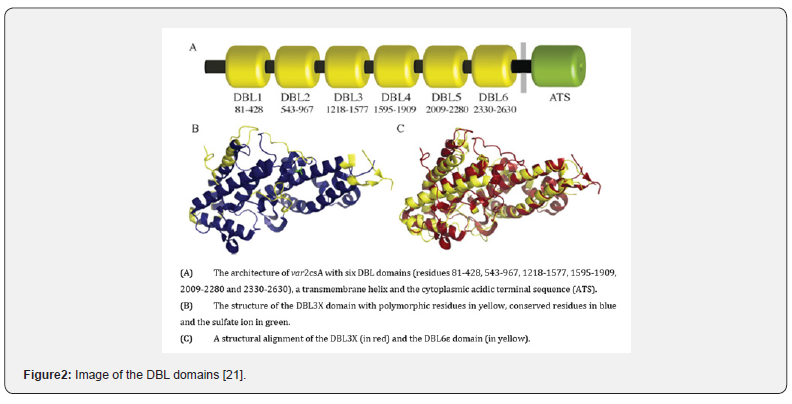
The structure of the DBL3X domain has been shown [22,23] to have an ɑ-helical scaffold similar to those observed in DBL domains from the invasion proteins like erythrocyte-binding antigen 175 (EBA-175) and the Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC) - binding protein [24,25].
It has also been shown that full length recombinant var2csA binds specifically to CSA with nanomolar affinity, and that the CSA- binding site lies in the N-terminal part of the protein [26]. The core CSA- binding site lies within the DBL2X domain and part of the flanking interdomain regions, in contrast to the idea that single domains do not possess the structural requirement for specific CSA binding. They added that the x-ray scattering measurement revealed CSA- binding DBL2X domain is situated in the center of the structure.
Materials and Methods
Materials
The following computing resources and items were used:
Compounds: The protein data bank (PDB) structure of the receptor chondroitin sulfate A (PDB ID: 3bqk) in its raw and prepared forms is shown in Figure 4. Structures of some of the ligands used are shown in Figures 3
Hardware and Software: This work was carried out on windows 8.1 Pro with processor: Intel® Core (TM) i5 CPU M 520 @ 2.40GHz having installed memory (RAM): 4.00GB (3.86 GB usable) on system type: 64 bit operating system although 32-bit Windows Vista operating system also work well. PyRx docking software version 0.8 for Windows [14]. PyRx is open source software to perform virtual screening. It is a combination of several softwares such as AutoDock Vina, AutoDock 4.2, Mayavi, Open Babel, etc.
PyRx uses Vina and AutoDock 4.2 as docking softwares. In this study, AutoDock Vina [27] was used. Discovery studio (Discovery Studio: v20.1.0.19295), Pymol (Pymol stereo 3D quad buffer) and ICM Browser (Molsoft MolBrowser 3.8-7d) were used to examine structural properties and study binding interaction between receptor residues and ligands. SwisADMET, and Molinspiration cheminformatics were used for evaluation of drug-likeness of the ligands and Toxtree [28] was additionally used to determine the toxicity and safety profile of the ligands.
Databases and Applications: Protein data bank (rcsb.org) and PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) were used to download the chemical structures of the receptor (3bqk) and those of the ligands. Canonical SMILES and other information about the ligands and the receptor were extracted from PubChem. Toxtree, Toxicity Estimation Software Tool (TEST), SwissADMET, Molinspiration and Lazar Toxicity Predicter were employed to test various toxicity and safety parameters of lead compounds.
Methods
Retrieval of Macromolecule: The structure of the macromolecule-chondroitin sulfate A (CSA) was retrieved by searching in the protein data bank (PDB) (rcsb.org/ structure/3bqk); downloaded and saved as a PDB format. Retrieval of Liands: Molecules constituting the ligands screened belong to the same enzyme commission (EC) class of CSA and were downloaded from rcsb.org as Excel file. In the file, the ID values of all the class members were copied and pasted on a page “download ligand” site in the PDB in order to generate their corresponding ideal structure data file (SDF) formats. The “launch download” application of PDB downloaded and channeled the ligands into a folder (ligands) that was created on the desktop. Some of the ligands are presented in Table 1.
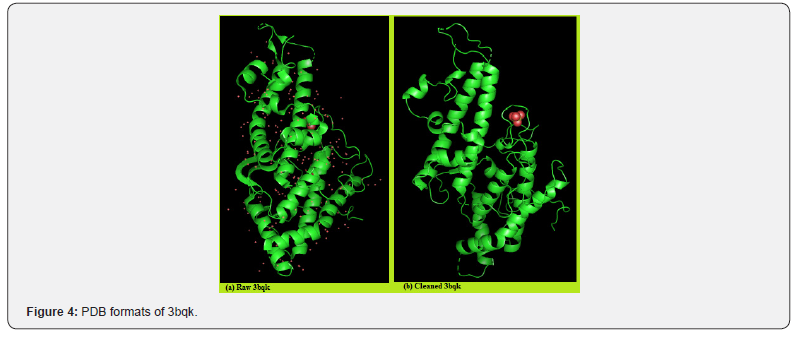
Target Preparation and Docking Process: The x-ray structure of the receptor (3bqk) was downloaded from protein data bank (rcsb.org), cleaned from hetatoms in discovery studio and resaved (Figure 4). The input ligand files were also prepared for virtual screening by converting them to PDBQT file format when they were imported into PyRx software as chemical table file (SDF). Following a series of steps, the library of the ligands was docked into the active site of 3bqk in the PyRx platform using Amber Van der Waals in the active box of 17 x 15 x 17. Autodock Vina took each ligand and bonded its different conformations to the receptor molecule (3bqk) to get the binding energies in different orientations of each ligand. Each ligand has nine different binding orientations starting from 0 to 8.
Validation of Docking Process: Docking was repeated three times on the same system specifications for the purpose of process validation and all returned minimal variation (P<0.01 data not shown) in uff energy, binding energy and RMSD values.
Binding Analysis: Discovery studio (Discovery Studio: v20.1.0.19295), Pymol (Pymol stereo 3D quad buffer) and ICM Browser (Molsoft MolBrowser 3.8-7d) were all used to analyze binding interactions between residues of 3bqk and the ligands.
Drug likeness: Toxtree, Toxicity Estimation Software Tool (TEST), SwissADMET, Molinspiration and lazar toxicity predictions were variously employed to test toxicity and safety parameters of lead compounds.
Results and Discussion
Results
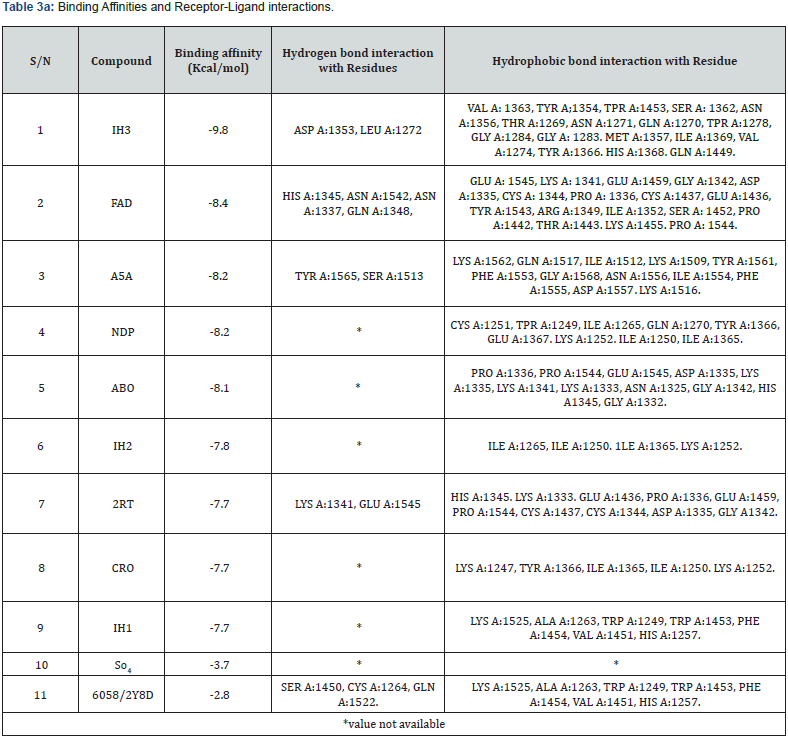
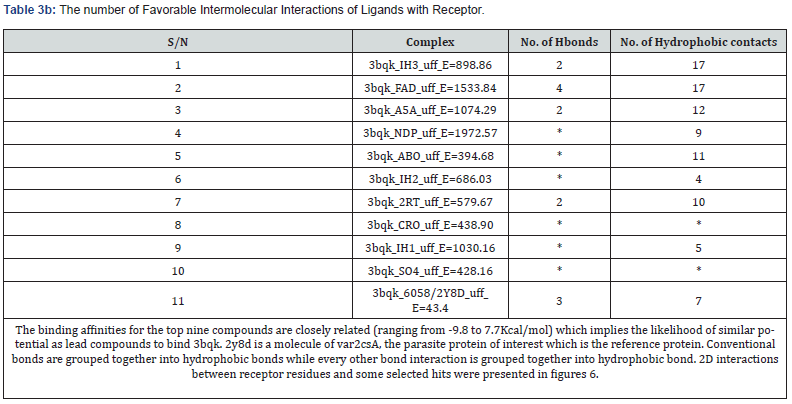
Analysis of Docking Result: A library of 90 compounds in the same EC class with chondroitin sulfate A, known to interact with pCSA was generated from rcsb.org. Compounds in the library demonstrated good binding affinity with many having higher binding affinity to pCSA (3bqk) than 2y8d a var2csA molecule and SO4, a functional species in chondroitin sulfate A (Table 2).
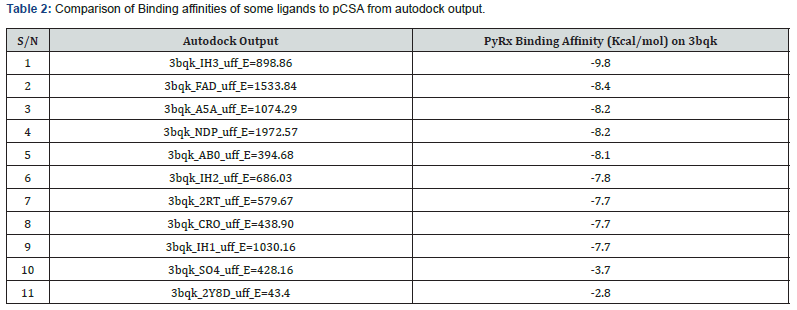
The first 75 ligands and SO4 have binding affinity higher than that of 2Y8D. This implies that var2csA can be displaced from pCSA in preference for molecules which have higher binding affinity. 2Y8D and SO4 which have their highest binding affinity as-2.8Kcal/mol and -3.7Kcal/mol also ranked 719th and 655th respectively. For this study, only the first nine ligands with the highest binding affinity (-9.8 to-7.7Kcal/mol), 2y8d and SO4 were selected for the target analysis. The complex formed for some of the ligands are represented in figure 5, the complexes have different structural modification from the SDF format seen in Figure 4 except for SO4 which it is not a valid selection for binding analysis. It is not a chain, molecule or a multiple residue object.
Analysis of Binding Interactions: Receptor residues interacting with SO4, 2y8d and the top nine selected ligands as seen in Discovery studio and Pymol are listed in Table 3a.
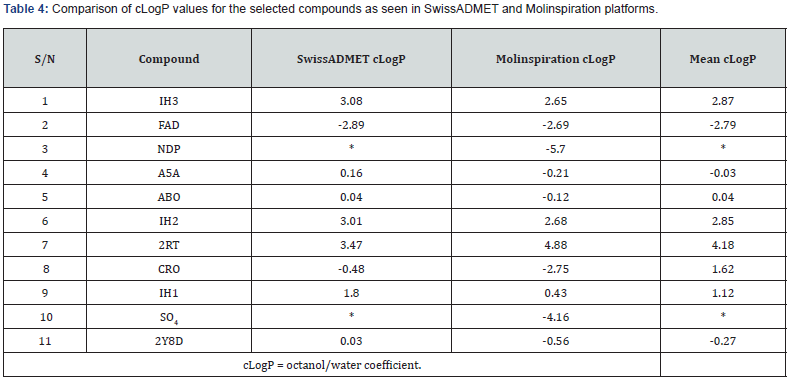
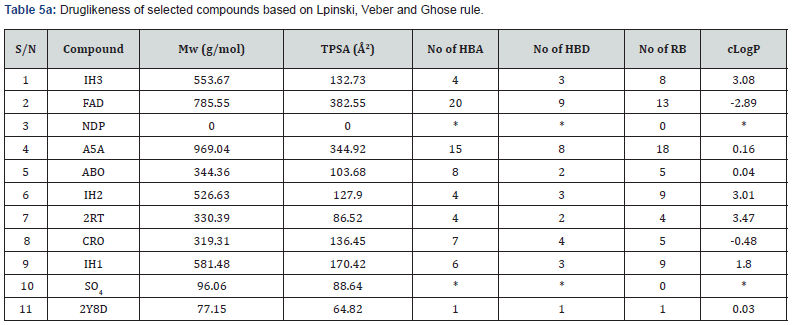
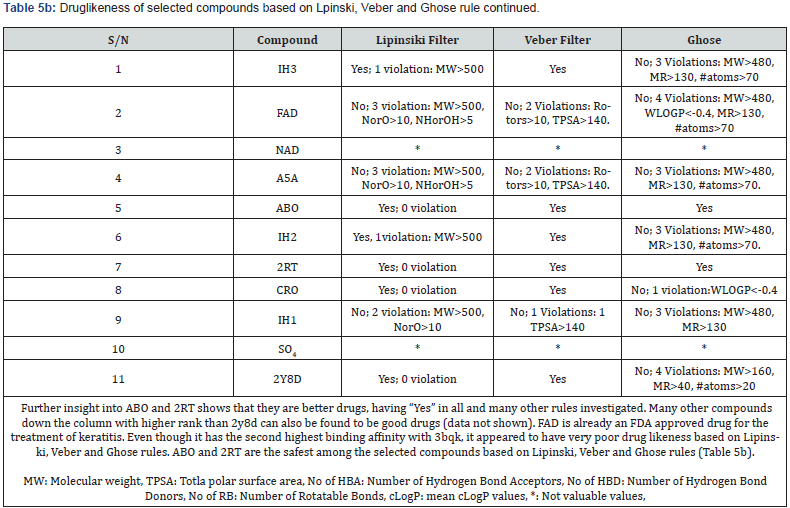
Evaluation of Drug likeness and Organ Toxicity of some Selected Hits: The lipophilicity for selected compounds is as shown by the values of their consensus logP in Table 4. Drug likeness of the compound’s Tables 5a & 5b.
Discussion
All the ligands in this study yielded their lowest binding energy at their first binding modes (0). The reliability of this study was ascertained by triple - docking of the ligands with the receptor (pCSA) and it was found that both the first, second and the third dockings maintained the same values in all parameters and for all binding modes (P < 0.01 data not shown), giving IH3 and FAD as the first two ligands with the lowest binding energy as shown in table 2 and implicitly, the ligands of choice to bind placental chondroitin sulfate during in vitro and in vivo evaluations. The binding affinities of the top nine compounds on var2csA target are closely related that they lie within a close range of -9.8 to -7.7Kcal/ mol indicating that their potential as lead compounds for 3bqk is comparable. Auto Dock reproduces nine different protein -
ligand complexes for which the structure of the macromolecule was known, without prior knowledge of the binding site but here only the result from the first binding orientation was presented since it is the one with the highest binding affinity, the full binding orientations and their RMSD values for all the ligands are available on request. The RMSD for the first binding orientation is always 0. The binding affinity and the RMSD value collectively determine the ranking of the molecules.Analysis of Binding Pattern
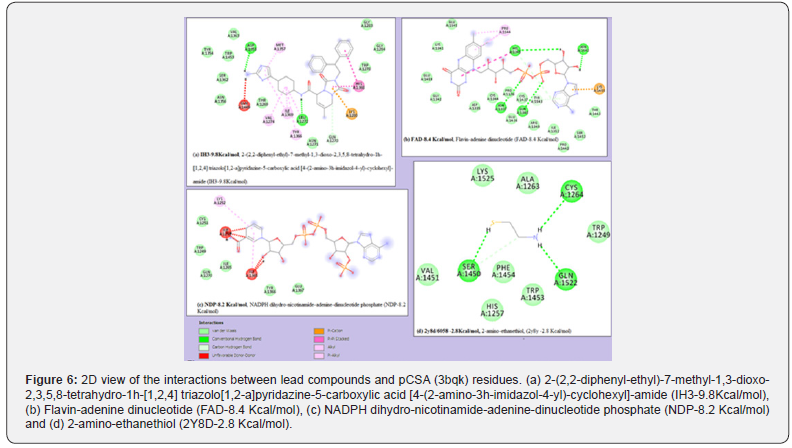
Considering their binding interactions, FAD had the highest number of favorable hydrogen bonds with receptor residues but shares equal number of hydrophobic contacts with IH3 (Table 3a & Table 3b). FAD is a drug already in used to treat eye diseases caused by vitamin B2 deficiency, such as keratitis and blepharitis (Drugbank, http://www.drugbank.ca/). Some other compounds like NDP, ABO, IH2, CRO, IH1 and SO4 possess no hydrogen bonds but have good number of other hydrophobic contacts except CRO and SO4 which do not have any significant favourable bonds with receptor residues based on observation from Discovery Studio (Figures 6).
Drugability of Compounds
No correlation was observed between lipophilicity and the interaction with the receptor by considering cLogP values and number of conventional bonds (Tables 3b & Table 4). However, for FAD, NDP and A5A, interaction with the receptor is correlated with low lipophilicity while 2RT has high cLogP value. The compounds with high cLogP values used their polar functional groups to interact with the receptor. FAD, 2Y8D and IH3 exhibited good hydrogen bond interaction with var2csA receptor of placental chondroitin sulfate A possibly due to their polarity.
Screening the compounds for drug likeness using Lipinski, Veber and Ghose filters, FAD, A5A and IH1 did not satisfy the requirements for a safe drug in all the filters used. However, only ABO and 2RT suitably satisfied the conditions for drug likeness in all the filters and therefore likely the safest (Table 5b). Notwithstanding these observations, all the compounds selected can be relatively safe since the unsatisfied molecules tend to violate 1 or 2 conditions in 1 or 2 of the three filters. Again, FAD which violated almost all the conditions in all the three filters is already in the market for other medical uses.
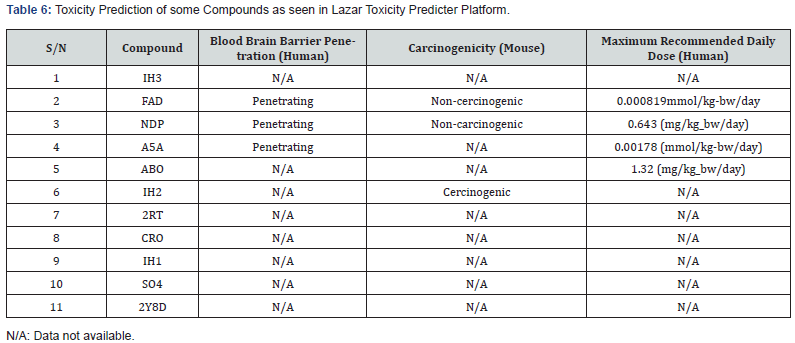
Based on toxicity prediction of some compounds in Lazar Toxicity Predicter, FAD, NDP and ABO penetrate the human blood brain barrier (Table 6) indicating possibility of central nervous system toxicity. But this could also be an advantage for the compound to access the brain to elicit their pharmacologic activity in the event of susceptible cerebral malaria. They also tend to be non-carcinogenic in mouse model based on observations from the same platform.
Summary of Findings, Conclusion, and Recommendations
Summary of Findings
In this study, an extensive search was carried out in silico to discover non recombinant substances that could serve as vaccines or adjunct treatment for pregnancy associated malaria (PAM) also known as placental malaria (PM). Ligands (or small molecules or drugs) with activity against chondroitin sulfate were extracted from designated drugs and proteins databases. The ligands were screened against a receptor (pCSA, PDB ID: 3BQK) to isolate molecules that can favourably bind it thus displacing or inhibiting binding of var2csA, a Plasmodium falciparum (P.f) protein usually deposited on the surface of P.f- infected erythrocytes that enhances the adhesion of the parasite carrying cells to the endothelium of tissue vasculature, thereby tethering them away from splenic destruction.
Ninety ligands were screened out of which 75 were found to have higher binding affinity with pCSA than var2csA, with binding affinity ranging from -9.8 to -2.8 (Table 2, complete data not shown). Out of this number, the best nine ligands (IH3, FAD, NDP, A5A, ABO, IH2, 2RT, CRO and IH1,) whose binding affinities ranged from -9.8 to -7.7 were isolated for further in silico evaluations. Their analysis showed that four compounds (IH3, FAD, A5A and 2RT) had hydrogen (strong covalent) bond interaction with 3bqk while five (NDP, ABO, IH2, CRO and IH1) had no hydrogen bond with 3bqk. One compound (CRO) does not have both hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds with 3bqk, yet it has high binding affinity with the receptor. This was possible because, the compound may have used its polar functional groups to make the interaction. The same is applicable to SO4 (a sulfate ion) which also do not have any hydrogen or hydrophobic contact with the receptor. 2Y8D had both hydrogen bond and hydrophobic bond interactions with the receptor (Table 3a & Table 3b).
In silico drug ability testing of the 9 selected compounds including SO4 and 2y8d indicates that only four compounds (ABO, 2RT, CRO, and 2Y8D) based on Lipinsky, Veber and Ghose rules perfectly satisfied drug likeness conditions (Table 5b). That means 2Y8D can be administered to mimic the parasitic form of it in binding placental chondroitin sulfate A. FAD violated all the rules for a safe drug but it has been approved for use in the treatment of eye diseases caused by vitamin B2 deficiency, such as keratitis and blepharitis. Lazar Toxicity Predicter (Table 6) showed FAD, NDP and ABO to have ability to cross blood brain barrier and non-carcinogenic.
Conclusion
Following the analysis and observations so far, all the 9 selected compounds including SO4, 2y8d and all the rest of the compounds screened deserve further in vitro and in vivo evaluations to determine which compound has the best in vivo activity against placental malaria and safe for human use.
To Know more about Novel Approaches in Drug Designing & Development
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/napdd/index.php




No comments:
Post a Comment