Carbon dioxide is a non-flammable, inexpensive and
non-corrosive substance that due to its properties is a suitable solvent
for supercritical fluid extraction.co2 critical temperature
is 31.06oC and its critical pressure is 7.386MPa. Due to its low
critical temperature, thermal degradation of food components is not
occurred. For extraction of compounds with high molecular weight,
supercriticalco2 extraction is a suitable technology. In dairy processing industry, supercriticalco2
extraction, in comparison to pasteurization process, has vast
applications, such as using as enzymatic and microbial inactivation
agent; producing bicarbonates, carbonic acid and hydronium in milk
carbonation reduced liquid production, extraction and fractionation of
fat and cholesterol by which, higher quality products and solvent free
residues were produced. On the other hand, supercriticalco2
technology systems have the advantage of operating as batch,
semi-continuous and continuous mode. In this research, different
applications of supercriticalco2 extraction for some dairy products are reviewed in detail.
Keywords: Supercritical carbon dioxide Dairy product Extraction Green solvent
Abbrevations: PAA: Peracetic Acid; SCT: Short-Chain Triglycerides; MCT: Medium Chain Triglycerides; LCT: Long-Chain Triglycerides
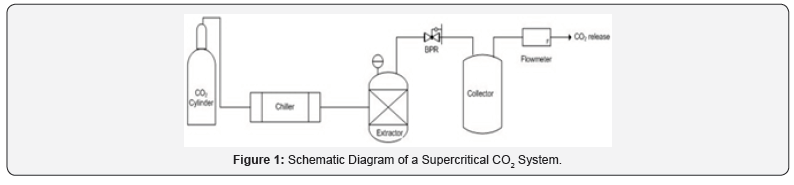
In supercritical fluid extraction, under certain
temperature and pressure, as some chemicals are good solvents for some
solutes, the required extraction happened. For each solvent, above its
critical pressure and its critical temperature, it becomes
supercritical. CO2 critical temperature is 31.06oC and its critical pressure is 7.386 MPa. CO2
as a non-flammable, non-corrosive and inexpensive substance is a proper
solvent for supercritical fluid extraction. On the other hand, as CO2
critical temperature is low, thermal degradation of food components
during extraction is prevented [1]. For extraction of compounds with
high molecular weight, supercritical CO2 extraction is a suitable technology (Figure 1). This system has CO2
pump, pressure regulator, a chamber for keeping the sample, anda
collecting vessel. A heating zone is also required in which the liquid
would be heated to supercritical condition and subsequently for
solubilizing the sample to diffuse into it. From extraction column,
dissolved material is sent to separator and extracted part was settled
out. In the last stage, carbon dioxide is cooled, recompressed and
discharged to atmosphere or recycled to the process [2]. In the food
industry, supercritical CO2 is an ideal solvent; as it is
inert, cheap, available, odorless, tasteless and safe solvent. Due to
its near ambient critical conditions, supercritical CO2 is an appropriate choice for thermo-labile and
non-polar natural products. In comparison to pasteurization process, in dairy industry, supercriticalco2 process has various applications; it is suitable for reduction in microbial substances. As a consequence, a product with better shelf life and greater
organoleptic properties would be obtained.
Dairy products are consumed all around the world. Due to
their high nutritional value, they were considered as healthy
choices. It is predicted that by 2024, approximately 36%
increase in global consumption of different dairy products
would be observed [3]. In order to have safe milk consumption
and stable shelf-life, milk must undergo thermal processing. As
conventional high-temperature processes may lead to change
in nutritional and organoleptic characteristics, in recent years,
alternative non-thermal technologies are required; such as
supercritical carbon dioxide. In order to destroy microorganisms
(while keeping nutritional content), supercritical carbon
dioxide technology is used. Although due to high equipment
and operational cost, industrial application of supercritical
processes could be an obstacle [4-6].
In conventional food/medicine pasteurization process,
bioactive compounds may be destroyed by conventional
thermal process. In the food industry, various compounds at
their supercritical state were used; the most common one is
CO2. By reducing pressure, it can be omitted from food matrix
and be circulated to the system. This is the main reason that
supercritical CO2 technology is known as an environmentally
friendly one. Due to low critical temperature of CO2 this technology can
be used near room temperature which minimizes any probable
changes in the nutritional and physicochemical characteristics
of food and prevents degradation of thermosensitive and volatile
compounds. Moreover, as CO2 has moderate critical pressure,
minor investment costs are required for this process. In dairy processing, supercritical CO2 technology has many
applications; such as [7-11]:
a. Using as enzymatic and microbial inactivation agent.
b. Producing bicarbonates, carbonic acid and hydronium
in milk carbonation reduced liquid production.
c. Extraction and fractionation of fat and cholesterol by
which, higher quality products and solvent free residues
were produced.
Supercritical CO2 technology systems have the advantage of
operating as batch, semi-continuous and continuous mode. An
effective contact between CO2 and dairy sample was occurred
in semi-continuous and continuous systems. As CO2 saturation
is very rapid, enzymatic and microbial inactivation was more
effective; as a consequence, operating time and manufacturing
costs were reduced. CO2 pump and pressure regulator are main
compartments of a batch system. An exhaust system is also
implemented to release the pressure after the process. For
controlling the cooling or heating temperature, a temperature control apparatus is established which could be a water bath,
oven or autoclave. In semi-continuous process, vessels are
connected in series; some of them are pressurized and the rest
are in constant pressure. In this configuration, processing time
was reduced, and energy recovery was allowed. In continuous
apparatus, dairy sample and CO2 is mixed and passed through
the high-pressure pump. Praxair developed a high-pressure
CO2 pilot plant for milk treatment at different temperatures,
pressures and CO2 concentrations.
As CO2 can have influence on the quality of semi-hard
cheese, current researchers were focused on its use in modified
atmosphere packaging. Recently, the effect of ripening condition
and composition on CO2 solubility was studied [12]. It was
observed that in temperature range of 2-25oC, there is a linear
relation between CO2 solubility and temperature. Moreover, salt
content was increased from 0 g/100 g to 2.7 g/100 g, by which
CO2 solubility was decreased. On the other hand, fat content has
influence on CO2 solubility coefficient [13] which confirmed
that CO2 has effect on aqueous and fat phase, for the latterco2
solubility was increased with temperature. Another application
of supercritical CO2 technology is for microbial growth control
in mozzarella cheese. Using 100ppm of peracetic acid (PAA) in
combination with supercritical CO2, yielded maximum reduction
of Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores. As mozzarella cheese
has worldwide popularity and consumption, these findings have
vast application for the cheese industry [14]. Supercritical CO2
technology is also applicable in low-fat cheeses production; such
as Cheddar and Parmesan [15,16] and Gouda-type [17]. Cheese
matrix, temperature, pressure and CO2 mass flow are important
parameters that affect lipid removal.
Different researchers studied supercritical CO2 technology
effects on milk properties. For food products, supercritical CO2
technology reduced the pasteurization or sterilization time and
minimized thermal degradation of thermo-labile compounds
(such as vitamins) [18]. It is worth mentioning that for milk,
its effect on vitamins degradation must be studied in detail.
Acidified milk, in comparison to heat-treated milk, showed
better preservation to retinol, 𝛼-tocopherol and 𝛽-carotene [19].
Due to acidification and solvation properties, supercriticalco2
affect milk protein as well; the probable mechanism for this
phenomenon is binding the obtained carbonic acid with calcium
ions [20].In the process of supercritical CO2 treatment of milk,
casein precipitation is an obstacle after which a dairy product
containing cheese would be obtained [21,22]. The precipitated
casein has industrial application. It was reported [21] that for
fractionation and precipitation of concentrated protein solution,
supercritical CO2 technology is a suitable method. All around
the world, whey beverage consumption is increasing [23,24].
It is reported [25] that whey proteins, in comparison to caseinare more resistance to high pressure and supercriticalco2
technology is capable of changing the structure of whey proteins.
Alkaline phosphate (as a milk endogenous enzyme) is used as a
criterion of effectiveness in milk pasteurization. Centi et al. [26]
used supercritical CO2 to inactivate alkaline phosphate in milk.
They studied the effect of pressure (8-18MPa), temperature
(30, 50, 70oC) and mass ratio ofco2 to milk (0.05 and 0.45
wt.%) during 30 min. At 70oC, 80 MPa and 0.45 wt.% the best
inactivation rate of alkaline phosphate was obtained as 98.2%.
This finding confirmed that supercritical CO2 technology is
applicable for alkaline phosphate inactivation in milk.
In 1987, for increasing shelf life of dairy products,
supercritical CO2 use was proposed [27]. In recent years, in dairy
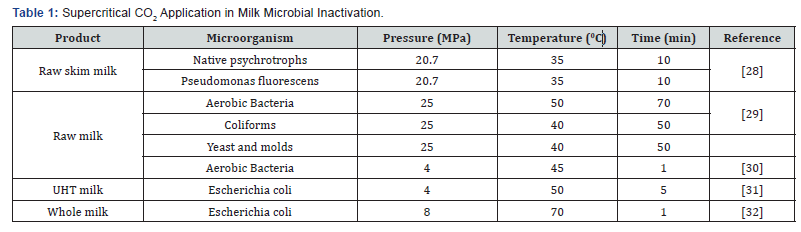
(with emphasis on milk) products, the use of supercritical CO2.for microbial inactivation was studied (Table 1).
In dairy products, spore-former is an important
contaminant as it affects food quality. Moreover, it facilitates
product spoilage as it decreased its commercial shelf life [33].
The effect of supercritical CO2 on milk spore’s inactivation
was reported in some researches. Werner and Hotchkiss [34]
evaluated the existence of Bacillus cereus spores at different
operating conditions (i.e. temperature: 15, 30, 35 and 40oC;
pressure: 10.3, 24.1, 48.3 MPa; CO2 concentration 0, 3.66, 132 g/
kg milk). All researches proved that supercritical CO2 technology
has the ability to inactivate microbial contaminants in milk;
although milk fat content, bacteria age, equipment type, and
operating parameters are important factors that have influence
on microbial inactivation rate. Hence, in dairy production, for
the application of supercritical CO2 technology, the knowledge of
microbial inactivation mechanism is vital.
Chitra et al. [35] used supercritical CO2 technology to
develop dairy product with healthier lipid profile. Temperature
(40-80oC) and pressure (15-25 MPa) were considered as
operating parameters; the optimum values for cholesterol
removal from whole milk powder were 68oC, 20.7 MPa, 6 lit/
min ofco2. Approximately 22.8% of cholesterol content was
removed, while free fatty acids, lightness amount and solubility
indicator were kept unchanged. In recent years, various
methods were investigated for cholesterol removal from foods
[36-38]; such as blending animal and vegetable fat with each
other, steam distillation, supercriticalco2 extraction, silica
gel- or carbon active- based adsorption, complexation with
𝛽-cyclodextrin, enzymatic treatment by cholesterol oxidase
and cholesterol reductase for cholesterol degradation and use
of cholesterol decomposing microorganisms such as Nocardia
and Rhodococcus. Among these methods, supercriticalco2
technology has various advantages, the most important of which
are high efficiency, rapid extraction fluxes, lower risk for thermal
product degradation, and higher nutrient retention [39,40].
It was reported that at moderate dynamic time increasing
operating pressure and decreasing extraction temperature
enhanced cholesterol removal [41-43]. For instance, increasing
pressure from 100 bar to 250 bar, cholesterol extraction wasincreased. On the other hand, by raising temperature from 40oC
to 57.5oC, cholesterol extraction was decreased and beyond
57.5oC a slight increase was observed in cholesterol extraction.
For dynamic extraction time, an increase from 2.5 h to 3 h
resulted in higher cholesterol extraction yield and from 3 h to
3.5 h yielded to lower insignificant cholesterol extraction yield.
As a concluding remark, for cream powder, optimum operating
parameters are 75oC, 204 bar and 3.5 h by which 39% reduction
in cholesterol content was observed [44].
Supercritical fluid extraction is a technique for lipid
fractionation and vitamin isolation. It was reported that
supercriticalco2 technology is applicable to dairy products
for vitamins A and E removal from powder [45,46]. In order to
reduce the negative effect of water content of milk on extraction,
Berg et al. [45] tested Hydromatrix as a water adsorbent. As a
result, in 80min, from 0.5 g sample, all vitamins A and E were
extracted. Ramos et al. [47] used supercriticalco2 technology by
which milk fat was fractionated into four different parts; namely
short-chain triglycerides (SCT), medium-chain triglycerides
(MCT), long-chain triglycerides (LCT) and cholesterol. It was
found that polychlorinated biphenyls are predominantly in SCT,
MCT and cholesterol fraction of milk fat.
Yu et al. [48] reported the application of supercritical
CO2 technology for anhydrous milk fat. Milk fat obtained
by supercritical CO2 technology affected rheological and
physicochemical properties of butter. Shukl et al. [49] reported
that the resultant butter has lower moisture content and
cholesterol and higher melting points. In order to produce valuable substances that have industrial
application, supercritical CO2 technology is a good candidate
as it is capable of extracting lipophilic food compounds [50].
Moreover, supercritical CO2technology has the capacity to
effectively inactivate microorganisms [51].
Supercritical fluid extraction as a green technology is
following all future regulations of health, safety and environment.
Supercritical fluid extraction has the ability to provide high
solubility, improved mass transfer rates and increased selectivity,
hence it has application in many industries. As a concluding
remark, in dairy industry, supercriticalco2technology is a good
option for keeping nutritional quality and inactivating important
enzymes. More research is needed to evaluate supercritical co2
influence on main intrinsic factors of dairy food processing such
as decreasing milk protein allergenicity.









