Reviews and Research - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
Influencing the general public response to pandemics is a public health priority. The preventive behaviours (e.g. wearing masks and reducing aggregation) that help in reducing the spread of pandemic found insufficiently followed across different regions, during recent pandemic influenza, 2009-10 H1N1 pandemic, including the current COVID-19 onslaught. Regional difference in public’s preventive intervention observed, owing to cultural values variables. Across the continents 209 COVID-19 pandemic affected countries reportedly adopted standard preventive protocol for COVID-19, but the pandemic spread, and onslaught showed different patterns in different countries. This human habit of maintaining or not maintaining physical distance is a result of a country’s culture which is rooted in its national heritage and traditions and the current pandemic scenario provides an opportunity to study the flexibility and adaptability of cultures between pandemic responses, on a governmental and societal level. In this study culture was defined using Hofstede's dimensions Individualism/Collectivism. An exploratory case-study methodology was taken after employing a post- positivist approach. The study findings indicated collectivism encourages faster and more effective COVID-19 responses and hence suggest cultural adjustments for the purpose of infectious disease preventive intervention.
Keywords: Culture; Individualism; Collectivism; Public health
Introduction
Influencing the general public response to pandemics is a public health priority. The preventive behaviours (e.g. wearing masks and reducing aggregation) that are effective in reducing the spread of pandemic found insufficiently followed across different regions, even during pandemic influenza, 2009-10 H1N1 pandemic, among others. Regional difference in public’s preventive intervention observed, owing to cultural values variables. Understanding the impact of social elements at the effect of pandemic assault across communities necessitates not just experimental observations, but also a conceptual framework for investigating and interpreting such observations. Societal individualism/ collectivism is one idea that could be useful as a guiding principle in this scenario; and the topic subsequently discussed with suitable references. Now to focus on the Coronavirus Disease 2019, as unfolded all over the world, and caused one of the most serious public health crises in recent times. Isolating actions as Social distancing, lockdowns, and other suggested and adopted as protective behavioral mechanisms to facilitate the avoidance of parasitic transmission along with other methods of managing local parasitic infections. However, in this pandemic, the enormous differences in transmission outcomes between countries and territories constitute a striking phenomenon. Social scientists suggest that the cultural difference of collectivism versus individualism could largely explain this divergence. Collectivist as opposed to individualistic values are important attributes of intercultural variation.
In this study culture was defined using Hofstede's dimensions Individualism/Collectivism. An exploratory case-study methodology was taken after employing a post- positivist approach, which was affected by Yin [1] and Noor [2]. This procedure is appropriate for the taking after reasons: i) the consider includes an observational examination of a developing marvel, which is the utilize of social media; ii) the consider accumulates realities to impartially degree event of certain design; and iv) the think about increases in value diverse elucidations of individuals on their encounters. Interestingly, the Parasite Stress Theory of Values [3-5] implies that the historical occurrence of infectious diseases may have played a role in the development of Individualist and Collectivist cultural differences. Societies with a high caliber of pathogenic stress were more liable to develop a collectivist culture that accommodates as a gregarious aegis against infectious disease spread, whereas societies with low caliber of pathogenic stress developed the individualistic value systems [3]. If this is true, modern societies with highly individualistic cultures may be more vulnerable to infectious diseases than more collectivistic societies. Another study [6] revealed that individualistic communities have had more infection disease outbreaks and zoonotic disease outbreaks in recent times but did not find a correlation for emerging infectious disease events.
The SARS CoV-2 situation reports of March 2021 brought out by world health organization (WHO) [7] indicate 209 pandemic affected countries across the continents adopted, by and large, uniform responses for pandemic control, but the spread and onslaught of COVID-19 has shown different patterns in different countries. Due to international variances in pandemic reactions on a governmental and societal level, the era of pandemic gives a chance to study the flexibility and adaptability of cultures. Due to the pathway of disease transmission through close patient contact, COVID-19 may be owing to close contact with the general population. This is where the culture of the susceptible population become evident and their behavior need detailed scrutiny. For instance, Italy was attributed to have a culture of close interaction (physical intimacy) as compared to Japan (culturally maintaining greater physical distance). Dissonantly the French saw social unification as a threat to the state, whereas Japanese culture intends to support the government’s response to COVID-19.
This human habit of maintaining or not maintaining physical distance is a result of a country’s culture which is rooted in its national heritage and traditions. Any attempt to abruptly change the behavior in order to prevent pandemic spread is impractical and will be met with public opposition, as has been proved in various countries.” The collective programming of the thoughts that separates the participants of one class of humans from another” is how culture is described [8]. As a result, population behavior and psychological elements that influence the said programming may be influenced in part by a country’s culture, which could be important in understanding Covid-19’s spread and mitigation. Indeed, a recent assessment found various social and behavioral traits, including cultural norms- that could help with the COVID-19 pandemic response, and encouraged researchers to cover gaps urgently [9]. There is also the pertinent issue of individualistic and collectivism cultural approaches of different countries that shape citizen’s cognitive processes. In general, individualism emphasizes non-public freedom and achievement. Individualist culture therefore gives social popularity to non-public accomplishments inclusive of critical discoveries, innovations, extremely good inventive or humanitarian achievements and all moves that project an individual. Collectivism, in contrast give importance to positioning individuals in bigger group. It whips up conformity and discourages individuals to balk and show up.
Individualism is said to hold sway in Western Europe and North America with their complex, stratified societies emphasizing independence and variety while collectivism is mean to thrive in Asia, Africa, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, in which agreeing on social norms is essential and jobs are interconnected [10]. For extra collectivistic societies like India, the self is described relative to others, is involved with belongingness, dependency, empathy, and reciprocity, and is centered on small selective coterie of fellow individuals in common business on the price of out-groups. Noted scientist Professor Geert Jan Hofstede put forward with six basic issues called dimensions of culture expressed on a scale that runs roughly from 0 to 100. His Collectivism-Individualism World Map provides a glimpse of nations’ cultural trait (Figure 1).
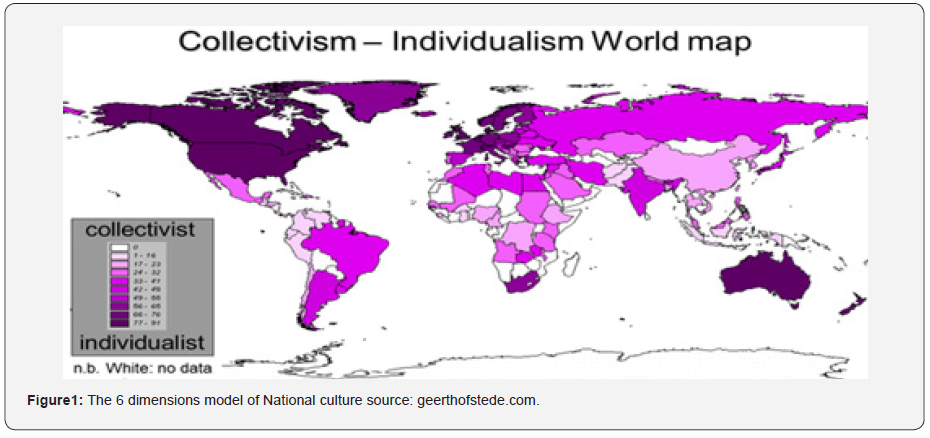
Hardin’s traditional article “The tragedy of the commons” [11] gives a prediction for the distinction among individualistic versus collectivistic societies dealing with the pandemic. Hardin defined a social ‘catch 22 situations’ wherein every decision-maker in a network is higher off performing egocentrically. Still, if others acted likewise without problem for the cumulative effect on society, “the commons” are in the end knocked down. Curiously, whilst not unusual place experience means that the virus will unfold extra fast in collectivistic societies because of their nearer and extra common social interactions, the mixture of way of life and Hardin’s principle endorse the opposite: the pandemic’s effect might be large in individualistic societies wherein human beings are less involved approximately in the greater good. COVID-19 has made it manner to almost every country within side the world and has but ended in very exclusive outcomes.
Epidemiologists have proposed lots of reasons for this variance, which includes variations in demographics, urbanization, excellent of health systems, the innate environment, and the rate of government responses [12]. Nevertheless, it is able to be argued strongly that way of life additionally matters. Because consensus is extra conveniently carried out in collectivist societies, their conditions are better for introducing speedy and effective motions to include disease containment. An investigation posted in February 2021 [13] researchers studied the connection among the individualism -collectivism size through the use of Hofstede’s cultural size version and the quantity of COVID-19 instances and associated deaths of all 69 countries, for which statistics became to be had in Hofstede’s national culture survey [14]. They conducted two simple correlations analysis and compared the variables among 36 Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries and then performed identical correlations evaluation at the whole pattern at the same time as controlling eight applicable variables, i.e. days considering the facts that outbreak of the pandemic, percentage of population over 65 years of age, democracy index, Gini index, percent of finances for healthcare, human longevity, population density and general COVID-19 tests per million.
Taken together, those consequences counseled that the greater individualistic a society is, the greater it suffered from COVID-19 associated instances and deaths. As a result, it may be claimed that cultural differences between countries are equally as important in determining adherence to epidemic prevention measures and, as a result, a society’s susceptibility to COVID-19 outbreak. The virus has spread practically every country on the planet, yet the results have been wildly disparate. It is arguable that culture plays a considerable role. It has been observed that collectivist cultures are more likely to reach an agreement, they are better suited to putting in place swift and effective disease control measures. In collectivist societies, social networks are also more localized and directed around people’s intimate relationships (typically their extended family). This causes natural social bubbles, reduces social mixing and diversity, and hence inhibit virus’s transmission.
According to studies, having a more individualistic culture leads to more innovation and progress since those societies value social workforce more [15]. But there are also disadvantages, as Hofstede pointed out individualist societies are at a disadvantage in terms of swift collective action and coordination. This is because residents are encouraged to hold opposing viewpoints, express themselves, and challenge and debate decisions. As a result, achieving the necessary agreement for policies to succeed may take longer. Individually, cultural values can influence basic decision such as whether or not to wear face mask or maintain social distance. According to studies, persons in areas of the United States with a history of colonialism and more individualistic culture are less likely to wear face masks and keep physical distance in public venues.
It is possible to evaluate the country-wise COVID-19 incidences based on the national data publicly available. The discrepancies between individualistic and collectivist countries, as well as their differing response to pandemic containment, are most obvious when looking at data from the onset of the pandemic. There is a direct correlation between COVID-related mortality per capita and individualism scores in countries. Furthermore, studies and actual evidence demonstrate that collectivism promotes a faster and more effective COVID-19 response. Given the circumstances, individualist countries should make major attempts at cultural adaption in that direction, especially during outbreaks of diseases. The speculation of pathogen prevalence, or the parasite stress model [3-5], states that people living in areas with greater incidence of infections are more likely to become collectivist in the long run than people living in areas with fewer incidence. The aftermath of COVID-19 is likely to be something never witnessed to world citizens. A new social order is likely to emerge, a new structure of the society, a paradigm shift in human relationships.
To Know more about Annals of Reviews and Research
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php






