Nutrition & Food Science - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
Present exploration depicts rare species milk as the
new source in search of novel starter cultures i.e. lactic acid bacteria
(LABs). Camel milk itself is very nutritional and rich source of
initial feed to infants. The term probiotics is very popular from the
last few decades so as the result search of new sources for the hunt of
novel probiotic strains increased. Efficient probiotics fulfill the
current market demand for the development of new industrial products.
This study focuses on the significance of rare species milk i.e. camel
milk and the essential probiotic attributes concerned for starters might
be used in industrial applications.
Keywords: Camel milk; Probiotics; Micro flora; Lactic acid bacteria;
Introduction
In today’s life every single (human being) is
consuming the functional foods in the form of dairy or non-dairy
products. Functional foods comprised of probiotics i.e. live bacteria.
Etymologically probiotics are pro (for) and bios (life). According to
FAO probiotics are defined as “live microorganisms which when
administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host”
[1]. Lactic acid bacteria genus considered to be safe and exhibit the
properties to be called as probiotics. In current market scenario as the
demand of probiotics is increasing so as the demand of new starter
cultures for the product development. Therefore, to find the new sources
is very important for the isolation of novel starter cultures. Among
the dairy sources many rare species Milk might be used as a source, and
one of them is camel milk. In India vast diversity of mammalian species
are
present but our society totally depends on cow and buffalo
milk for the initial nutrition only because no one can access the
milk from other thousands of species. And it is due to the fact
of lack of knowledge and awareness regarding the benefits of
rare species milk. The worlds camel population is 23.9 million
out of which 0.45 million is contributed by India [2]. Different
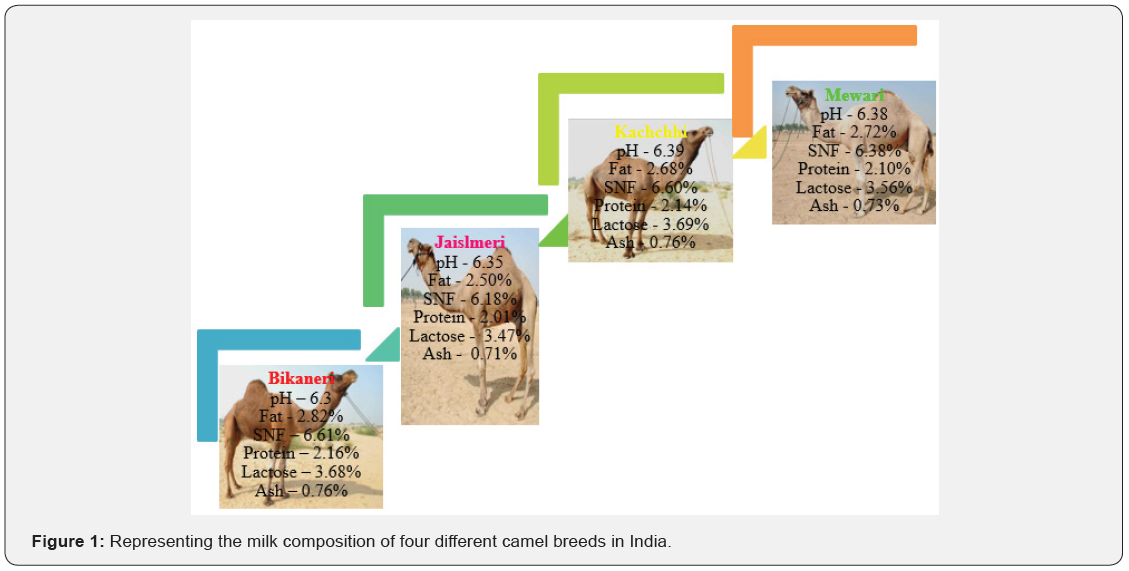
breeds of camel are present in India (Bikaneri, Mewari, Kachhi
and Jaisalmeri) [3]. Being a ship of the desert camel does
tolerate harsh climatic conditions and even in the scarcity of
water they produce more milk with longer lactation period
other than any species. Camel milk being rare species milk
is very rich in nutrients like proteins, minerals and vitamins.
Milk composition values of different breeds are shown in
(Figure 1). It specifically contains lot of protective proteins
and immunoglobulin’s which helps in improving the immune
system. It lacks the allergic proteins which are present in cow’s
milk. This is the solution towards the cow milk allergies, this
might act as a substitute as a weaning feed for babies. Even for
adults this rare milk is very valuable and beneficial for health
because it is good in many disorders like allergies, autism and
even in cancer.
With all these good prospects of camel milk its indigenous
micro flora is also rich in LABs (lactic acid bacteria) which are
termed as a safe species group of bacteria or GRAS (generally
recognized as safe) [4,5]. LABs are known for their probiotic
potential and they might use as starter cultures for dairy and
non-dairy product development. The examples of LABs with
probiotic application are Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus
brevis, Lactococcus lactis, Bifidobacterium and many more. LABs
are gram positive and catalase negative species which are able
to produce lactic acid as an end product from fermentation.
Further these strains might act as a probiotic feed for weaning
babies and come up as the solution of wholesome food for the
nutrition in growing stage. It is predominant to comment that
probiotic potential of bacteria is very much strain specific. It is
very important to recognize and identify the bacterial species
so that it might be apt for industrial applications.
Probiotic Attributes and Associated Health Benefits
It is mandate for potential probiotic; bacterial species must
exhibit some probiotic attributes within and exert beneficial
effects on the host. Major traits to be called as probiotics are
determined by in vitro tests:
a. Acid and bile salt tolerance is important criteria for
strains;
b. Bile salt hydrolase activity;
c. Cell surface hydrophobicity;
d. In vitro cell adhesion to mucosal epithelial surfaces;
e. Antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria;
f. Antibiotic resistance [1].
These in vitro parameters are the prerequisites for the
probiotic strains and shown in Figure 2. As far as dose of
probiotics is concerned, the lowest concentration 106 CFU/mL
is consumed daily for the visible good probiotic effect. Different
probiotic mechanisms are associated with the human health
which may include the production of antimicrobial substances
like bacteriocins, acidic pH of gut, and competitive adherence to
mucosal epithelial surface, providing the gut barrier functions
as well as enhancing the immune system [6]. There are
clinically proven evidences that actually prove the associated
health benefits of the probiotics. According to Russo et al. [7]
and Orlando et al. [8] probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain
GG (LGG) and Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM0212 showed
a significant anti proliferative role and inhibit human gastric
cancer cells and three colonic cancer cells lines including HT-
29, SW 480, and Caco-2 [7,8]. The probiotic mechanism for
decreasing the proliferation of cells and treatment still needs
to be understood and more research is required. Probiotics are
also helpful in allergies by moderating the allergic response.
Allergic reactions occur when an immune system reacts with
an allergen. Numbers of bacterial cultures were studied are
very limited for their ability in the treatment and prevention
of allergies in infants. Studies showed that L. rhamnosus GG has
been successful in preventing the occurrence of atopic eczema
in infants, when delivered to mothers who had already firstdegree
atopic eczema, allergic rhinitis or asthma [9]. Health
benefits of probiotics are not limited there are other; they
contribute in reduction of cholesterol levels and eventually
leads to reduction in coronary heart diseases, autism and
bacterial vaginosis in women’s. The mechanism of probiotics
behind the reduction of cholesterol level in serum is due to
the presence of BSH activity which helps in absorbing the
cholesterol from the gut. These properties are strain specific
in nature and vary with strain to strain. There is more need
of valuable research regarding the clinical evidences of health
benefits of probiotics.

Conclusion
It can be concluded from the present study that, rare
species milk are the good source for the isolation of novel
LABs. Utilization of rare species milk needs to be considered
by creating the awareness among the society. As far as their
probiotic activity is concerned, remains to be validated in
future studies.
To know more about Nutrition & Food Science Journal
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/nfsij/index.php
To know more about Juniper Publishers
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php




No comments:
Post a Comment