Bioequivalence And bioavailability international journal Juniper Publishers
Authored by Gaurav Agarwal*
Abstract
The present research has been undertaken with the aim to formulate and evaluate the semi-herbal gel containing Clindamycin Phosphate and aloe vera. The gel was prepared by using polymer Acrypol 940, Tefose 63 as an emulsifier, Labrafil M as a co-emulsifier and Transcutol P as a penetration enhancer and methyl paraben, propyl paraben as preservatives and required amount of distilled water. FTIR analysis was performed to ensure the compatibility of the actives and the excipients. Then, the formulation is evaluated for % drug release, HPLC and particle size analysis through zeta potential, Zeta Perkin Malvern which was found to be 402nm. % drug release in the formulation was found 100.06%. The skin pH was maintained by using diethanolamine and was set at 5.5. The physiological parameters of formulations pH, viscosity, spreadibility were determined. Stability studies were carried out as per ICH guidelines through accelerated stability studies.
Keywords: Nanogel; Transdermal delivery; Anti acne; In vivo studies
Introduction
Transdermal delivery in the form of nanogel is a promising and challenging task that enables the delivery of drug into the deep layers of skin by providing maximum penetration and making the formulation more effective. The entry of drug through the stratum corneum may follow the intercellular, transcellular or appendageal route. The intercellular route is more common pathway of the drug permeation through the skin [1]. Transdermal route has proven to be more effective route of administration then injectables and oral route and provides more convenience thus increasing patient compliance and avoiding first pass metabolism respectively. Transdermal delivery provides controlled, constant administration of the drug; it allows continuous input of drugs with short biological half-lives and reduces the undesirable side effects.
This route of administration faces few limitations like drugs having high molecular weight fail to penetrate the stratum corneum if their nature or structure is not modified. Similarly, drugs with low or high partition coefficient fail to reach systemic circulation. Also, drugs with high melting point, due to their low solubility both in water and fat show low permeability. Besides having limitations transdermal drug delivery shows many advantages and the most important advantages are that it bypasses hepatic first pass metabolism, enhances therapeutic efficiency and maintains steady plasma level of the drug [2].
Nanogels based drug delivery system is highly biocompatible and biodegradable due to this characteristic it is highly promising field now a days. Other properties of nanogel include high drug loading capacity, good permeation capabilities due to extreme small size, can cross blood brain barrier, nanogels are able to solubilize hydrophobic drugs and diagnostic agents in their core or networks of gel. Nanogel or polymeric nanogel systems have better stability over the surfactant micelles and exhibit lower critical micelle concentrations, slower rates of dissociation and longer retention of loaded drugs and this type of delivery system usually does not produce any immunological responses. The most important character of nanogel is that it can load both hydrophilic and hydrophobic type of drugs and also charged solutes [3].
The effective barrier properties of the skin may prevent the entry of drug molecules from the external environment. Molecules may activate allergic reactions and the drug may be metabolized by microflora on the surface of skin or by enzymes in the skin. Clindamycin, a lincosamide antibacterial, has been found to be as effective as systemic tetracycline, topical erythromycin and topical benzoyl peroxide. Clindamycin is bactericidal to Propionibacterium acnes. Due to the inhibition of Pacnes the free fatty acid levels (break down product of sebum by Pacnes) on the skin surface also decrease. Clindamycin phosphate applied topically penetrates to a very great extent in to open comedones and thus produces a high percentage of sterile comedones [4].
In order to avoid the side effects of the drug i.e. clindamycin phosphate like redness and itching, aloe vera (a herbal component) has been added to the formulation which provides smoothness to the skin thus minimizing the side effects of the formulation. Aloe vera is a herbal component that has been used since ages to cure skin problems and has shown great stability and acceptability by majority. The efficacy of drug penetration and permeability may be increased through an effective approach of using co-emulsifiers and it has been shown from the studies that the nanogel along with co-emulsifiers gives improved dermal delivery properties and this work describes the preparation of formulation using pharmaceutically accepted ingredients.
Material and Methods
Clindamycin Phosphate was purchased from Gorang International and was provided by Laborate Pharmaceuticals India Limited, Panipat, India. Transcutol P, Tefose 63 and Labrafil M were obtained as gift samples from Gattefosse India, Mumbai. Aloe vera was purchased from Orchid Chemicals.
Method of Preparation of Nanogel
For formulation of Clindamycin phosphate and aloe vera nanogel, polymer and homogenizing speed play an important role. The basic procedure that was followed started by dipping Acrypol, Mtehyl paraben and propyl paraben in distilled water and was left over night and was heated at 70-80 °C, then clindamycin, Aloe vera and Trancutol P were added. After further heating, Tefose 63 and Labrafil M were added and the gel was centrifuged which was later homogenized at varying rotations per minute (up to 6000rpm).
Evaluation of the Formulation
Measurement of physical appearance and ph
The gels prepared were evaluated for pH and their physical appearances as appearance of gel is important so as to increase the patient acceptance. The color and state of gel states the acceptance of the gel by the patient [5].
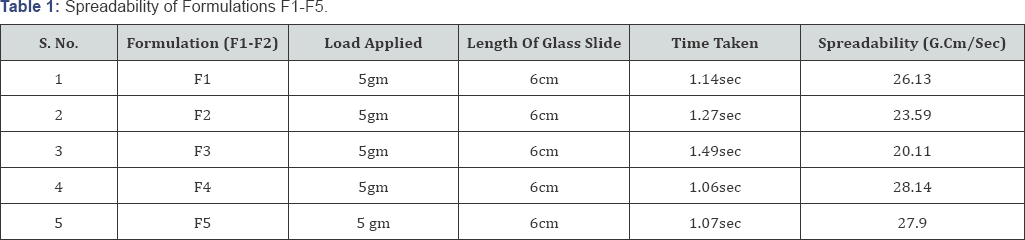
Determination of spreadability
The parallel plate method is most widely used method for determining and quantifying the spreadability of semi-solids [6]. Spreadability indicates the fineness of the gel. As the size of the particle is decreased, spreadability becomes better and increases, thus taking less time to spread shows the basic concept of spreadability. The bioavailability concept efficiency of a gel depends on its spreading value [7]. The following equation was used for the purpose
S = M x L/T
Where, S = Spreadability of the gel formulation
M = Weight (gm) tied on the upper plate
L = Length (cm) of the glass plates
T = Time taken for plates to slide the entire length
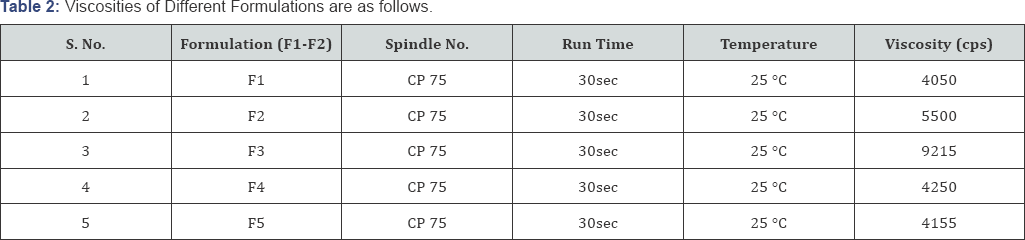
Viscosity Studies
The rheological measurements are determined to signify various properties of nanogels like association, entanglement and cross-linking. The viscosity determinations were carried out on Brookfield viscometer [8]. The range of an optimum viscosity is 5000-7500cps.
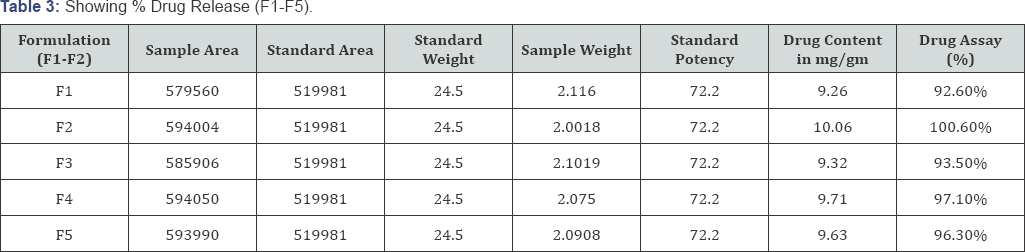
% Drug release by HPLC
HPLC, Shimadzu is used to identify and quantify drug. HPLC utilizes a column that holds the chromatographic packing material (stationary phase), a pump that moves the mobile phase through the column and a detector that shows the retention times of the molecules. Standard formula was used to determine the % drug assay content [9].
The formula used for calculation of drug in mg/gm is as follows:
Sample Area x Standard Weight x 100 x Standard Potency = mg/gm Standard Area 100 Sample Weight 100
The formula used to calculate the % drug release in the range is as follows:
mg/gm x 100 = % age drug release Claim
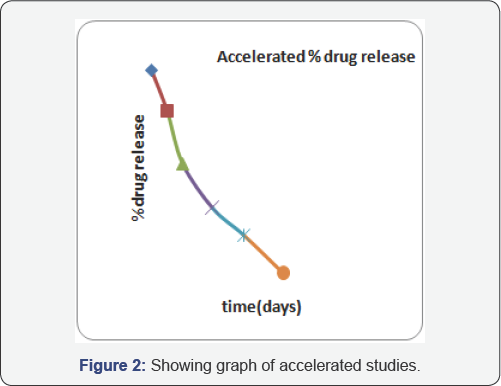
Measurement of particle size of the formulation (Zeta Potential)
For proper penetration of gel into the skin, the most important factor is its particle size which was measured through Zeta Potential. Particle size and zeta potential were measured by dilution of the formulation in distilled water using Zeta Perkin Malvern Zetasizer, UK [10].
FTIR Studies
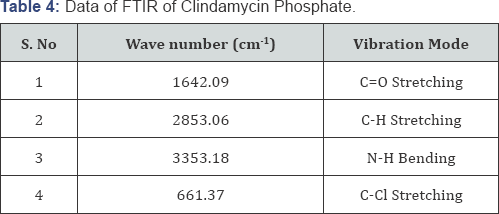
The main application of FT-IR spectro-photometry is the determination of the identity of a compound by means of spectral comparison with that of an authentic sample and verification of the presence of functional groups in an unknown molecule. Compatibility of the actives and excipients is evaluated from FT-IR [11]. The KBr pellet of approximately 1mm diameter of the drug was prepared by grinding 3-5mg of the sample with 100-150mg of KBr in pressure comparison machine. The sample pellet was mounted in FTIR, Nicolet-380, Thermo-USA compartment and scan taken at wavelength 4000cm-1 to 400cm- 1 .For analysis, IR spectra of the pure drug and aloe vera have been performed and no major differences were observed in the absorption peak pattern.
Stability Studies
Accelerated stability studies
Since the period of stability testing can be as long as two years, it is time consuming and expensive. The stability studies of formulated gel were carried out at 40/75(°C/RH) and at room temperature for one month the effects of temperature, humidity and time on the physical characteristics of the gel were for assessing the stability of the prepared formulations [12].
Results and discussion
Evaluation of the formulation
The nanogels were opaque to clear transparent in color with smooth in appearance depending upon the polymer used in the formulations. All the formulations were odorless and pH value of 1%w/v gels were found to be in range 4.5 to 6.5.
Determination of spreadibility
Spreadability of all the formulations was calculated using the formula as shown and the results according to the formula are shown in (Table 1).
Determination of viscosity:
The viscosity of the gel was determined using Brookfield viscometer (Table 2).
Determination of % drug release
Clindamycin phosphate can be analyzed at wavelength a using HPLC system with a 210nm detector and a 4.6nm x 25cm column that contains packing L7 having the flow rate of about 2mL per minute (Table 3).
Ft-ir spectroscopy, shimadzu ir spectrometer
The possible interaction between the drug and the ingredients used in the preparation of nanogel was studied by FTIR spectroscopy. The IR spectrum of the drug was recorded and the functional groups were interpreted as per the structure and were found to be appropriate or matching the structure of the drug (Table 4).
Determination of zeta potential
The prepared nanogel showed particle size of 402nm (range 230-400nm) after its dilution in double distilled water which is negligibly high than the nanoparticle size range. The zeta potential was determined for the optimized formulation by using Zeta Perkin Malvern Zetasizer, UK. The graph of zeta potential can be seen in (Table 5) (Figure 1).
Accelerated stability studies
Accelerated stability studies were carried out on optimized formulation that is F2 nanogel. The samples were stored at 40 °C ± 2 °C and 75% ± 5% (climatic zone IV condition for accelerated testing) for one month to access their stability. Parameters like appearance, feel on application, pH, viscosity and drug content were determined (Figure 2).
Discussion
The Clindamycin and aloe vera active constituents were evaluated for physical parameters and showed results within the range as per IP and USP. The gel was prepared and evaluated for Physical appearance, pH, spreadability and viscosity studies and finally % drug release was found. F2 formulation was evaluated best in all the tests and can be concluded as the best formulation which was further evaluated for stability studies.
Conclusion
It can be concluded from the current research work that the nanogel of Clindamycin and Aloe vera in combination can be successfully prepared and evaluated that was prepared by double emulsification method by using variable ratio of polymer, acrypol 940 and varying the speed of homogenization and the formulation was stable as per ICH guidelines. It was then subjected to safety studies through skin irritation studies which showed no significant irritation on skin of Swiss albino mice. From the results, it is clearly evident that the nanogel that has been developed is totally safe and stable and can be concluded by saying that the nanogel formulated by double emulsification method, for the treatment of mild to moderate acnes fulfils all the parameters.
To Know More About Bioequivalence
And bioavailability international journal Please Click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/mabb/index.php



Best Herbal Aloe Vera Body Lotion For Complete Care on Captain herbal store .this aloe vera herbal lotion is Use For moisturize your skin while soothing eczema, rashes, windburn, and other skin conditions and many more about this lotion Click here
ReplyDelete