International Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences
A 52 years old male nonsmoker, presented with a
history of shortness of breath, cough, hemoptysis and upper right upper
quadrant abdominal pain for the last one month. No history of loss of
weight or appetite. Patient was diagnosed six months ago as hydatid
disease of liver and lung and he was commenced on oral scolicidial agent
Abendazole by referring hospital. Computed tomographic scan of thorax
and abdomen Demonstrated large bilateral pulmonary and hepatic cysts
with typical radiological findings of hydatid cyst. Pulmonary cysts were
excised by staged procedure and later on hepatic cyst were drained by
interventional radiologist.
Keywords: Echinococcus granuloses liver; Lung; Hemoptysis; Hypertonic saline; Surgery
Background
Parasitic infestation by Echinococcus Granuloses was
described by Rudolphy in 1808 as a hydatid cyst also this is known as
echinococcosis and hydtasois [1]. There are four other species of
Echinococcus which can affect human but among all
Echinococcus Granulosus is the most common cause of zoonotic parasitic
infection (Table 1). Epidemiologically, this disease prevails almost all
over the world but there are endemic areas as Australia, New Zealand,
South and Central America, Middle East, Sub Saharan Africa, Russia,
China, Turkey [2,3].

Case
A 52 years old male smoker presented to our tertiary
care hospital with history of cough and hemoptysis. He was diagnosed six
months ago in the referral hospital as case of hydatid disease of lung
and was commenced on Albendazole 800 mg daily. He had scattered
hemoptysis for 3-4 times in a month but prior to admission he had
massive hemoptysis. On clinical examination he had dyspnea with the
respiratory rate of 24/min, no cyanosis or jaundice, breath sounds were
decreased over right hemi thorax. Laboratory tests revealed Hemoglobin
(8gm/dl), liver enzymes Alanine Transaminase (ALT) 28U/lit
Aspartate Transaminase (AST) 16U/lit, Alkaline phosphatase
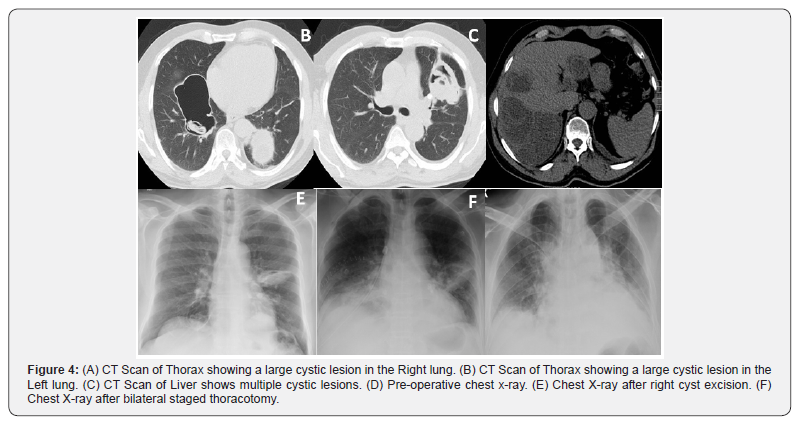
300 U/lit. Chest radiograph and CT scan of thorax and upper
abdomen showed large bilateral pulmonary and hepatic cysts.
Immunoglobulin G for echinococcus was positive. As the patient
had massive hemoptysis and was symptomatic urgent surgery
was planned. Surgical approach was right thoracotomy and we
found a very large cyst densely attached and compressing the
lung parenchyma. A purse string suture was placed and in the
center of cyst and surrounding lung tissues were covered with
gauze soaked in hypertonic 14% saline. A 14 F catheter was
inserted in the cyst and tightly snugged to avoid any spillage then
200 ml of 14% hypertonic saline was installed in the cyst cavity
and left for five minutes after that fluid was sucked, catheter was
removed and purse suture snugged. With meticulous dissection
cyst was removed in total sparing the lung parenchymal tissues
(Figures 1 & 2). The left side cysts were removed as staged
procedure after four weeks in similar fashion. Histopathology
report showed dead daughter cysts and no live parasite (Figure
3).


Discussion
Echinococcosis also known as hydatisosis is the most
common parasitic disease caused by larval cestodes. This
parasite harbors in two hosts: primary and intermediate to
complete its life cycle. Livestock animals like sheep, goat, horse,
pigs, camels as well as humans are intermediate host while
the Carnivorous animals like wolves, dogs, are definite host
(Figure 4A-4F). Humans are infected accidently by ingesting the
vegetables, fruits and water contaminated by soil with dog stool
containing eggs. Echinococcus eggs can survive for a year outside
in the atmosphere and are the main source of contamination
[4-6]. On ingestion eggs hatch to oncosphere larva in the small
intestine thereafter, enter in to the blood stream and is carried
to the liver by portal circulation or can by pass to pulmonary
system and then develop to metacestodes. These fluid filled
cysts are composed of hundreds of protoscolices, which are the
source leading to formation of daughter cysts or mature worm
(2-3 mm long). This life cycle is usually completed in 2-7 weeks.
Human to human spread is not possible as carnivores’ (definite
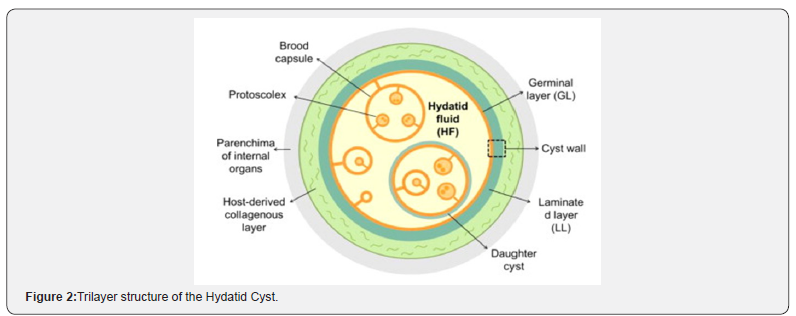
host) is required to complete the life cycle. Hydatid cysts are tri
layers, (pericyst, laminated and germinal) filled with nutritious
fluid that promote larval growth [7,8] (Figure 5).

The best diagnostic modality is imaging chest x-ray and
CT scan of thorax and abdomen [9,10]. Serological methods,
Weinberg complement fixation and Casoni tests were used in the
past and their yield is very poor. ELISA and IHA are most widely
used serological tests [11]. Patients with pulmonary hydatid
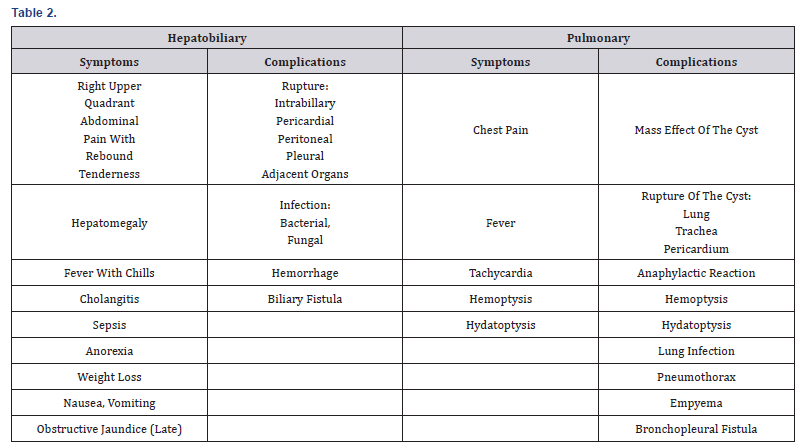
disease are initially asymptomatic. Most of the symptoms are
either due to mass effect of cyst on neighboring structures or
rupture of cyst leading to anaphylactic reaction, hemoptysis,
hydatoptysis, infection, pneumothorax and empyema (Table 2).
Clinically patient can present with chest pain, fever, tachycardia,
hemoptysis, and hydatoptysis. Pulmonary hydatid cysts increase
in size faster than in other parts of body probably due to elastic
nature of lungs and negative intrathoracic pressure [12-14].
Treatment is chemotherapy and surgery. The medical
treatment is very beneficial in patients with multisystem
(disseminated) disease and can be given as neodjuvant therapy
or adjuvant therapy in patients at risk of spillage during the
surgery. The commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs are
Mebendazole, Albendazole, Benz imidazole and Praziquantal.
Albendazole is preferred because of its better bioavailability
and the dose is 15mg/kg body weight per day in two daily
doses approximately 800mg daily dose for minimum 3-6
months. It is not recommended in pregnancy particularly in
first trimester due to its teratogenicity [15-18]. Horton et al.
[19] treated 500 patients of Echinococcosis giving those 800 mg
of Albendazole daily two and half cycles with 14 days interval.
After evaluation of 250 patients only 47 required surgery and
resected specimen demonstrated that only five patients have
viable parasite. Recurrence rate in patients who received preoperative
Albendazole as compared to those who did not
receive Albendazole was 18.75& 4.16 % respectively. In medical
literature Little et al. [20] reported recurrence rate of 22%,
Mottaghlan and sadi observed 11.3%. Medical treatment alone is
not enough to eradicate the disease once there are cystic lesions
in lung and liver [19,20].
Radical Surgical resection of host tissues and entire cyst is
mandatory if patient is symptomatic or any signs of infection
or invasion in to surrounding structures. Postoperative
chemotherapy for 1-2 years is recommended. Surgical approach
is designed according to the location of the cysts. Most common
surgical approaches are thoracotomy, median sternotomy
and video assisted thoracoscopic resection. The basic surgical
principal is that spillage of cyst contents should be avoided
and adjacent tissues should be packed with gauze soaked in
hypertonic saline solution (15%,20%) to avoid contamination.
In case of cyst rupture during surgery or if cyst is infected, after
the removal of germinal layer its recommended to wash the
cyst cavity with hypertonic saline solution [21]. Dekak et al.
[22] reported 202 patients who underwent surgery out of 422
cases. Enucleation, capitonage, segmentectomy, and lobectomy
were the procedures performed [22]. Biswas & Burhan et al.
[23] reported 26 and 24 cases respectively which were treated
surgically. Ashok et al. [24] reported 33 cases out of 72 who
required surgery [24].
Liver is the most common site of hydatid cyst formation, right
lobe and left lobes are affected 60-75% and 20% respectively.
Hepatic cysts generally remain asymptomatic for long time.
The most common complication is intrabillary rupture 3-17%
or rarely can rupture in to pericardial, pleural or peritoneal
cavity, and neighboring organs in 20-50% of cases. Sometimes
cysts develop secondary bacterial or fungal infection. The best
diagnostic modality is Ultrasound and Spiral CT scan. ERCP can
be helpful for diagnosis of biliary rupture or communication.
Liver hydatid cyst rupture can be categorized as contained,
communicating or direct. Reported incidence of communicating
rupture in to biliary system is 44-64% [25]. The patient with
intrabillary rupture present with right upper quadrant pain,
obstructive jaundice, fever, cholangitis and sepsis (Table 2).
There are multiple treatment modalities for the management
of liver hydatid disease and surgery is reserved for complicated cysts. Rupture of the cyst into adjacent organs, complicated
with biliary fistula, compression of adjacent vital structures
and cysts with infection or hemorrhage require surgical
intervention. Surgery is also recommended for cysts with
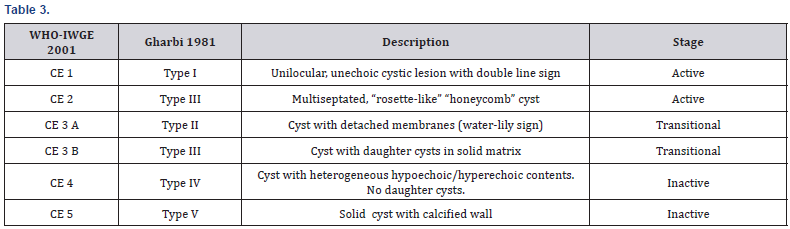
many daughter vesicles that are not amenable to percutaneous
treatment (WHO stage CE2 and CE3b) [26] (Table 3). If the cyst
diameter is more than 10cm and or percutaneous facilities are
not available then surgery is advisable. The other management
options recommended by WHO are drug therapy (Albendazole)
for stage CE1 and CE3 a provided the cysts are less than 3cm. If
because of any reason medical management is not feasible then
percutaneous treatment with puncture, aspiration, injection and
respiration (PAIR) is the alternative. Combination treatment
with PAIR and Albendazole is recommended for stage CE1 and
CE3 that are more than 5cm in size [27-29].
Conclusion
In conclusion we treated a patient who had simultaneous
hepatic and bilateral pulmonary hydatid cysts who presented
with hemoptysis and right abdominal upper quadrant pain. The
pulmonary hydatid cysts were resected as staged procedure and
liver cysts were treated with PAIR and Albendazole therapy for six
months. Our improvised technique of installation of hypertonic
saline in the cyst prior to surgical dissection is effective and safe.
To know more about International journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/cerj/index.php




Elegantly composed substance like this reestablishes my confidence in quality composition. I, at last, discovered the data I can concur on and use. Much obliged to you for sharing. For More Information Visit Here Stomach Problems Treatment
ReplyDelete