Trends in Technical & Scientific Research
Fault tolerance is in the center of distributed
system design that covers various methodologies. This research paper
aims to investigate different types and techniques of fault tolerance
which are being used in many real time distributed systems. The fault
can be detected and recovered by many techniques. Moreover, an
appropriate fault detector can avoid loss due to system crash or any
kind of failure in system. This paper provides a framework for detecting
fault in real time system which is supposed to be handled and processed
further by the help of coordinator.
Keywords: Fault Tolerance, Fault Detection, Real Time Distributed System, Processor faults, Coordinator, Actuators
Introduction
When multiple instances of an application are running
on several machines and one of the server goes down, there is a need to
implement an autonomic fault tolerance technique that can handle these
types of faults. Distributed Computing Systems consists of variety of
hardware and software components. Failure of any of these components can
lead to unpredicted behavior of system which results in failure to
guarantee availability and reliability of critical services [1]. A
failure occurs when a hardware component is broken and needs replacement
or a node/processor is halted or forced to reboot; or software has
failed to complete its run. Fault tolerance is the property of a system,
where system tends to work even in case of fault present in system.
When a fault present in real time distributed system
is not detected and recovered properly on time then it results into
failure of system. A task running on real time distributed system should
be feasible, reliable and scalable, real time distributed systems like
nuclear systems, robotics, air traffic control systems, grid etc. are
highly dependable on deadline. Fault present in system can be detected
by applying reliable fault detector followed by some recovery technique.
These systems must function with high availability even under software
and hardware faults. Hardware fault-tolerance is achieved through
applying extra hardware like processors, communication links, resource
(memory, I/O device) whereas in software fault tolerance tasks, messages
are added into the system to deal with faults. The main aim of fault
tolerant distributed computing is to provide proper solutions to these
system faults upon their occurrence and make the system more dependable
by increasing its reliability.
Real-time computer controller is typically provided
with sensors which will provide readings at periodic intervals and the
computer must respond by sending signals to actuators. There may be
unexpected or irregular events and these must also receive a response.
In all cases, there will be a time-bound within which the response
should be delivered. The ability of the computer to meet these demands
depends on its capacity to perform the necessary computations in the
given time. The paper is organized as follow: Basic Concepts and Types
of Fault is described in section 4 as background along with behavior of
failure systems, related works is described in section 5, The proposed
model or framework of fault tolerance in section 6, methodologies of
framework is described in section 7 and finally we conclude with
conclusion and future works in section 8.
Background
Basic concepts and types of fault
Basically system to be fault tolerant is much more
similar with concept of dependable system, and any system to be
dependable it must be available, reliable and secure. Following are few
terminologies that are very closely related to dependability of system
and its behavior. Fault can be termed as defect at the lowest level of
abstraction and there can be different failure in a system they can be
of following types [2].
Processor faults (Node Faults): Processor faults occur when the processor behaves in an unexpected manner.
It can be classified into three types:
a) Fail-Stop: Here a processor can both be active and
participate in distribute protocols or is totally failed and will
never respond. In this case the neighboring processors can
detect the failed processor.
b) Slowdown: Here a processor might run in degraded
fashion or might totally fail.
c) Byzantine: Here a processor can fail, run in degraded
fashion for some time or execute at normal speed but tries to
fail the computation.
Network fault: A Fault occur in a network due to network
partition, Packet Loss, Packet corruption, destination failure, link
failure, etc.
Physical faults: This Fault can occur in hardware like fault in
CPUs, Fault in memory, Fault in storage, etc.
Media faults: Fault occurs due to media head crashes.
Faults can be categorized on the basis of computing resources and time
a) Fault on basis of resources are:
• Timing failure
• Response failure
• Crash failure
b) Fault with respect to time are:
• Permanent: appear and persist until repaired
• Intermittent: appear-disappear-reappear behavior
• Transient: appear once and disappear
c) Failed System Behavior
A system can behave after failure in three ways such as
d) Fail Stop System
• No output when system fails
• Immediately stops to sending any message or event
• Does not respond any message receiving on network
• Any failure in system results a permanent fault
e) Byzantine system
• Not stop after failure but gives wrong output
f) Fail-fast system
• System behaves like a Byzantine system for some time
but moves into a fail-stop mode after a short period of time
• System does not perform any operation once it has failed
Motivation
The occurrence of fault in a system cannot be predicted and
even small changes or failure in system can lead to tremendous
effect. So, in order to make processing of transaction more reliable
for achieving better outcome of result even in presence of fault,
need of fault tolerance is essential which can avoid faulty system.
Objectives
To provide safety to the real-time system that is a system must
be designed in a way that if it is not working correctly, it will fail in
very safe manner.
Related Work
There are some important methods for tolerating fault in
various systems given by many authors in their research. According
to Alain Girault et al. [3]the Algorithm Architecture Adequation
(AAA) method will generate a static code automatically for real
time distributed embedded system. This method basically used for
processor failure with fail stop behavior. Luo et al. [4]mention that
TERCOS and DEBUS are the best approaches used to exploiting
redundancies in Fault-Tolerant and Real-Time Distributed Systems.
Girault et al.[3]mention that processor and communication link
failure can be tolerated by using offline scheduling technique and
generate a fault tolerate distributed schedule. Job scheduling is
one of the method in grid computing for scheduling a task. The
fault can be occur in loosely coupled job scheduling with job
replication scheme such that jobs are efficiently and reliably
executed can be tolerated [5]. In programming asynchronous
multiprocessing systems, the customary approach has been to
make process synchronization independent of the execution rates
of any components which means that synchronous algorithm
is required in which one process must wait for another to do
something before it processed ahead. These time- independent
algorithms cannot be fault-tolerant because a process could fail
by doing nothing, and such a failure manifests itself only as a
reduction of the process’s execution rate [6]. Leslie Lamport[7]has
made an additional assumption that the clock are synchronized to
keep approximately the same absolute time in order to show how
they can be used in solving the synchronization problems that
occurs in distributed systems and use of clock allows elimination
of acknowledgement message. If distributed system is really single
system, then the processes must be synchronized in same way.
Conceptually, the most easiest way to synchronize any process is
just to get them to do the same work at same time. In this paper
also they have implemented a kernal that performs a necessary
synchronization i.e. making sure that two different process do not
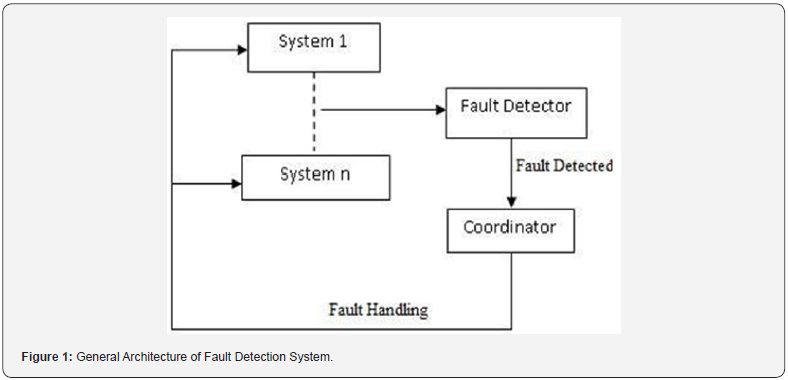
try to modify file at same time(Figure 1).
Framework
The proposed system consists of two major components:
a) Fault Detector and b) Coordinator
Fault detector
Fault detector is used to detect fault in a system and it runs
on each node in the user space. Fault Detector monitors all the
systems where system activities are classified into two of classes:
a) Normal type and
b) Anomalies type
Here system detector checks whether the activities are of
normal type or is of anomalies type. If the activity happens to be
of anomalies type then the Fault Detector sets an Alarm and next
step is handled by coordinator[8].
Coordinator
After detection of fault in a system, it is coordinator which is
responsible to carry out the further tasks. Once the fault is detected
in a system, coordinator gets the alarm from fault detector and
after getting those alarm, the coordinator must be able to take
corrective action within certain period of time. Finally, all records
are supposed to be recorded in the fault log table[9,10].
Method Development
Detecting and handling the Fault in the system is carried out in
the following 2 phases(Figure 2):
a) Monitoring Phase and
b) Corrective Action Phase

Monitoring phase
Monitoring task is performed by fault detector where task of
fault detector is to take input from systems. Once input is set in a
system then fault detector detects whether there is any types of
fault present or not. If fault is found then the system send those
occurrence of fault to the coordinator where corrective task is
supposed to be performed by coordinator, but if there is not any
types of fault present in system then further task is supposed to be
carried out by system.
Corrective action phase
This process is activated as soon as there is presence of fault
in a system. After detecting any sorts of fault in a system, the
coordinator gets alarm from the system once fault is detected.
After that coordinator isresponsible for handling those fault. For
handling the fault, the coordinator searches for the new node with
sufficient resources. It then requests that node to perform the task
and halts the process running is the fault node.
Conclusion
Fault tolerance has been an important issue from the
beginning of the phase. Several researches have been carried out
for solving this issue. Still it is a prominent issue in this area. This
paper deals with existing approaches to solve the problem of fault
tolerance. To address this issue, a framework has been designed
with its working mechanism. Furthermore, this model requires
to be validated which can be performed by using the simulation
process.
To Know More About Trends in Technical & Scientific Research Please click on:




No comments:
Post a Comment