AcademicJournal of Pediatrics & Neonatology Juniper Publishers
Authored by Zongezile Masonwabe Makrexeni*
Background
Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) is a post infectious, non-suppurative sequel of pharyngeal infection with streptococcal pyogens, or group a beta hemolytic streptococcus [1]. Rheumatic fever occurs in 3-4% of untreated group a streptococcal pharyngitis. Devastating complications of Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD) include severe valve regurgitation, heart failure, strokes and infective endocarditis, usually affecting both younger schools going and economically active, child bearing members of society [2].
Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD) is of global health significance. It is estimated that 15.6-19.6 million people live with RHD, with almost 80% of those residing in low and middle income countries, whilst it has become rare in high income countries [3,4,5] Rheumatic heart disease remains a preventable non-communicable disease [6].
Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD) is of global health significance. It is estimated that 15.6-19.6 million people live with RHD, with almost 80% of those residing in low and middle income countries, whilst it has become rare in high income countries [3,4,5] Rheumatic heart disease remains a preventable non-communicable disease [6].
The options for surgical management of rheumatic valve disease are valve repair and replacement with either bio-prosthetic or mechanical prosthesis. For patients with mitral valve stenosis an option is percutaneous mitral valve balloon valvuloplasty [10].
Percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty, has demonstrated good immediate and midterm results and has replaced surgical mitral commissurotomy as the preferred treatment of choice for rheumatic mitral stenosis in appropriately selected candidates [11].
Retrograde (Trans arterial) and antegrade (transvenous) approaches to percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty have been described. Currently, the antegrade approach with trans-septal catheterization is more widely used. It is usually performed through the femoral vein; however, the jugular venous approach has also been described [11].
Mitral valve repair is recommended over mitral valve replacement in the majority of patients with severe chronic mitral regurgitation who require surgery. Lower operative mortality rates, better preservation of left ventricular function, freedom from the hazards associated with anticoagulation, and continued growth of the valve in young patients are distinct advantages of mitral valve repair over mitral valve replacement [12].
Different techniques can be used to repair rheumatic mitral valve lesions: prolapse of the anterior leaflet caused by chordal elongation or rupture can be treated by chordal shortening, chordal transfer, or artificial chordal replacement; restricted motion of the anterior and/posterior leaflet can be treated by commissurotomy, splitting of the papillary muscles , resection of the secondary, or sometimes primary posterior chordae, posterior leaflet free edge suspension, leaflet thinning , and leaflet enlargement can be treated using autologous pericardium. Because mitral annulus dilatation is present in almost all patients with mitral regurgitation, concomitant ring annuloplasty offers more stability in valve repair, improving long term outcome [12].
Rheumatic heart disease remains a public health issue in developing countries. However, in the post-apartheid South Africa, there seems to be a decline in the prevalence of RHD [2,13]. Interestingly, there remain cases of rheumatic heart disease that require surgery in the Eastern Cape province of the country. There are no studies to best of our knowledge that have documented the clinical outcomes of surgery for paediatric rheumatic valve disease in South Africa.
Methods
This was a retrospective review of records of pediatric patients operated for rheumatic valvular heart disease in a tertiary hospital in South Africa; from January 2008 to December 2015.
Demographic data such as age, gender, geographical origin, surgical interventions and outcomes were analyzed.
Echocardiography study done post-operatively, one month, six months and one year after surgery and on further follow up was recorded. The International Normalized Ratio (INR) monitored in all the patients that were on war far in post-operatively was also noted. Record of secondary prophylaxis in all patients was recorded and documentation of administration route (intramuscular or oral penicillin) was made according to the Pediatric Cardiac Clinic protocol of Dora Nginza Hospital.
Statistical analysis and ethical clearance
Variables were reported as a mean (±standard deviation) or median (range). Nominal variables were compared using t test. Statistical significance was determined by using P value < 0.05. Ethical clearance was obtained from chief executive officer of Dora Nginza Hospital and the Health Research Ethics and Bio safety Committee of Walter Sisulu University. All the information obtained from the patient’s files was treated with strict confidentiality and no patients were prejudiced in any form.
Results
A total of 24 patients were operated for rheumatic valvular heart disease at Dora Nginza Hospital from January 2008 to December 2015. There were 14 males (58%) and 10 females (42%). The majority of patients operated came from the former Transkei region (OR Tambo district) (n=14; 58%) of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. The rest of the patients were from Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan and Sarah Baartman Municipality of the Eastern Cape Province. All the patients in this cohort were between the ages of 5-15 years.
Twenty patients (83%) presented with severe mitral valve regurgitation. Only two patients presented with mixed mitral valve disease (mitral regurgitation and stenosis). Four patients presented with severe aortic regurgitation. There were no patients with aortic valve stenosis.
All patients had echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular function pre- and post-operatively. There were 12 (50%) patients with dilated left ventricle (LVEDD>50mm) preoperatively. Of those, 9 (75%) patients had improved to normal left ventricular size (LVEDD < 50mm) post-operatively (p value < 0.05). There were 6 (25%) patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction < 55%) pre-operatively. Four of these patients had improved left ventricular systolic function post-operatively.
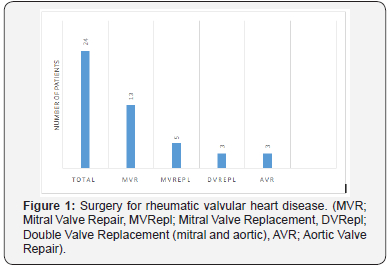
Regarding the type of surgery, thirteen patients (54%) had mitral valve repair; 5,mitral valve replacement; 3, aortic valve repair, and 3 patients had double valve (mitral and aortic valve) replacement (Figure 1). The On-X mechanical valves (by On-X Life Technologies, Cryolife, Kennesaw, GA 30144, U.S.A) were used for all the patients who had mitral or aortic valve replacement surgery. There were no patients that had surgical valvotomy or percutaneous mitral balloon Valvuloplasty. The average age at surgery was 9 years (5-15 years).
Four patients required re-operation with mitral valve replacement following failed mitral valve repair. There was one patient that had atrial flutter post operatively and this patient was treated with Amiodarone with good control of the arrhythmias. One patient died in this cohort due to a non-cardiac related cause (suicide).All the patients that had mitral valve and aortic valve replacement surgery were on anticoagulation with war far in therapy and had their INR levels monitored on a monthly basis.
All the patients in this cohort were on secondary prophylaxis.
Discussion
In the province of the Eastern Cape children continue to suffer from rheumatic heart disease that requires surgery contrary to what is seen in other provinces in the country [2,13]. Twenty four patients were operated for rheumatic valvular heart disease. The majority of patients were from the former Transkei region of the Eastern Cape (OR Tambo district) which is presumed to have high levels of poverty and therefore at a higher risk of developing RHD than the rest of the population in South Africa [14].
As shown in other studies, mitral valve regurgitation was the commonest presentation and as such the commonest indication for surgery in our patients with RHD [6-8]. The average age at surgery was 9 years in our cohort. This suggests that in areas with high prevalence of rheumatic heart disease, valvular surgery might be indicated much earlier. As reported elsewhere, paediatric patients with rheumatic heart disease present less commonly with valve stenosis or mixed regurgitation and stenosis as opposed to adult patients [8].
About 54% of our patients had mitral valve repair surgery for severe mitral regurgitation. As mentioned earlier, mitral valve repair is preferred over mitral valve replacement in patients with severe chronic mitral regurgitation requiring surgery [12]. This approach becomes more relevant in the developing countries. This is due to elusive management of patients with prosthetic valves as a result of limited financial and medical facilities, especially for anticoagulation monitoring or control [12]. And this preference is despite a relatively higher operative failure rate and re-operation rate in mitral valve repair in rheumatic valve disease compared to degenerative valvular disease [15,16] Lower operative mortality rates, better preservation of left ventricular function, freedom from the hazards associated with anticoagulation, and continued growth of the valve in young patients are distinct advantages of mitral valve repair over mitral valve replacement [12]. In our cohort only 13% of patients required re-operation due to failed mitral valve repair.
Double valve (mitral and aortic) replacement is generally not common surgery for RHD as there are few patients that present with severe mitral and aortic valve disease simultaneously [7-9] In our case series, and as shown in literature from other centers; there were only three patients (12%) that required double valve replacement. Percutaneous balloon mitral Valvuloplasty was not done in our patients because patients who had mitral stenosis also had mitral regurgitation and therefore were not good candidates for balloon valvuloplasty [17].
Ventricular dilatation due to severe mitral regurgitation was the commonest indication for surgery in this cohort. This is the commonest indication for surgery in patients with RHD [18]. There was statistically significant recovery of ventricular function in those patients that had poor left ventricular function pre-operatively. Pediatric patients generally have good surgical outcomes for rheumatic valve disease especially when they are operated on time. Even though 50% of our patients were operated with severely dilated left ventricles they had good outcomes post operatively. This might be due to the fact that the subjects were pediatric patients. This group tends to have good outcomes following surgery even with extreme ventricular dysfunction [18].
Study limitations
This was a retrospective chart audit of patients seen and operated in one referral hospital. Some parameters or measures of severity of disease like the New York Heart Association Functional Classification were not included in the study as there was poor clinical documentation to allow for this classification to be noted.
Conclusion
Children with rheumatic heart disease require surgery early for valve disease, and have good outcomes even if they are operated with severely dilated left ventricle due to severe mitral valve regurgitation. Rheumatic valve repair surgery maybe preferred surgery for eligible patients in sub-Saharan Africa, due to limited financial and access to medical facilities particularly for the added burden of long term follow up anticoagulation control in patients with mechanical valve replacement. RHD remains a burden in the resource-deplete Province of the Eastern Cape, contrary to the declining disease trends reported in other provinces in South Africa.
To
Know More About Academic Journal of Pediatrics & Neonatology Please
Click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ajpn/index.php
To Know More About Open
Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper
Publishers



No comments:
Post a Comment