Psychology and Behavioral Science International Journal Juniper Publishers
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the reliability and validity of the Ukrainian version of second version of the Emotional Schema Questionnaire (LessII; Leahy, 2000) and provide expected scores for nonclinical samples.
Objective: Emotional schema concept is developed for determining beliefs and attributions about emotions. The aim of this study was to examine validity and reliability of the Ukrainian version of “Leahy Emotional Schema Scale” (LESS).
Method: The sample consisted of 1230 people as statistical sample, 62 percent were male, and 38 percent were female. Respondent’s’ average age was 14-55 years old. Most of them including 39 percent had bachelor degree.
Result: The results of the study showed that due to the Cronbach’s alpha that is higher than 0.7, the reliability of all variables is desirable. Confirmatory factor analyses support the schema domains. We conclude that the LessII is a psychometrically sound instrument that can be used Ukraine in research on early maladaptive schemas. Further research is necessary particularly in larger clinical samples [1].
Keywords: Emotional schema; Emotional Schema Questionnaire; LessII; Reliability; Validity
Introduction
Emotional schemas
Emotion includes evaluation, feeling and paying attention to a situation. Emotions are usually behavior driving forces and, in most cases, they are an external component Leahy RL [2]. Emotions are multi-dimensional, and they exist in the form of subjective, biological, goal-oriented and social phenomena. The trace of emotions could be observed in all of experiences of individuals. Emotions caused by emotional schemas are observed in all behaviors, relations, cognitions and responses to conditions Leahy RL [2]. These schemas include a series of rules guiding individuals in specific situations [3,4]. In emotional schemas it is tried to highlight the emotions and emotional process approaches [2] and to emphasize on individuals’ interpretation of the emotions and planning done by the help of combination of core beliefs and emotional evaluations to evaluate and interpret individual’s adaptation to the environment [2]. According to Leahy, emotional schemas are those which the future final clinical model is based on. Researches have shown that there is a correlation between certain schemas and prevalence of psychiatric symptoms.
Emotions can be tacked in all experience of people. In all behaviors, relationships, and response of people to the situations, emotions derived from emotional schemas is observable [4]. In emotional schemas model, high efforts put on accentuate emotions and strategies of emotional process [5] and it emphasize on emotions and plans by which combining core beliefs with emotional evaluations that specifies this assessment and interpretation of a person compatibility with that condition [6].
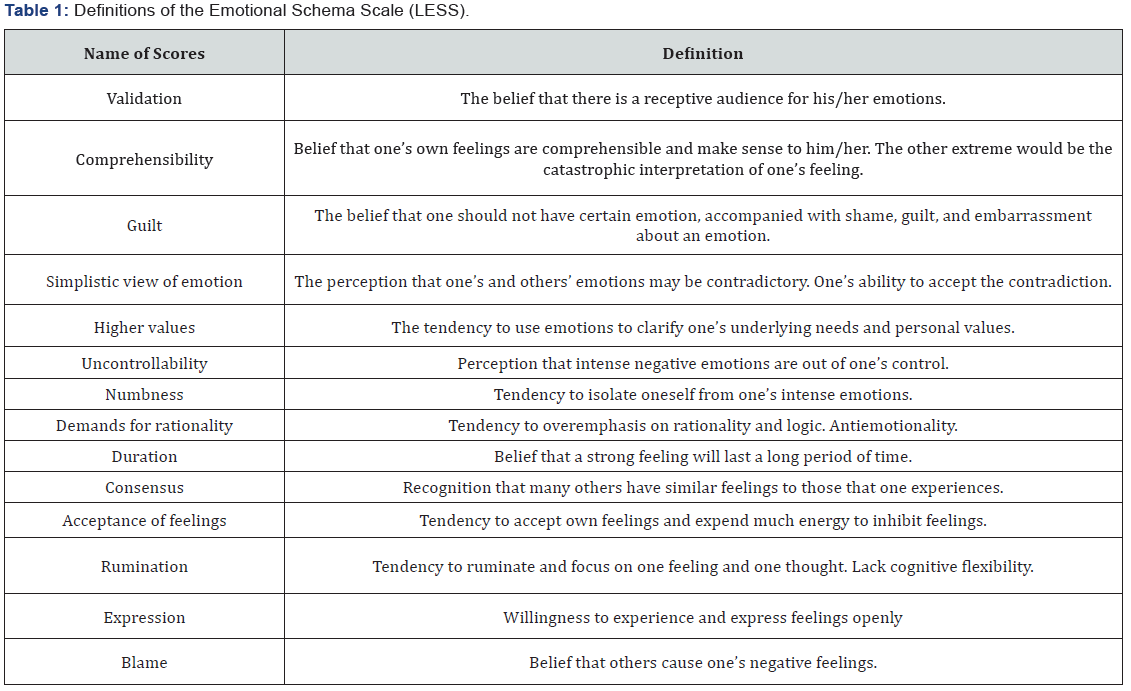
Participant responses are designed to evaluate the 14 emotional schema dimensions proposed by Leahy (e.g., simplistic view of emotion). Table 1 lists each of the dimensions and their attendant descriptions. The number of items used to evaluate the dimensions varies: acceptance of feelings utilizes seven items; rumination utilizes five items; comprehensibility, guilt, simplistic view of emotion, and consensus utilize four items; validation, higher values, control, and rational utilize three items; and numbness, duration, expression, and blame (Table 1).
Method
Demographic information
Results of demographic study indicated that out of 1230 people as statistical sample, 62 percent were male, and 38 percent were female. Respondent’s’ average age was 14-55 years old. Most of them including 39 percent had bachelor’s degree.
Descriptive statistic
Results of descriptive statistic indicated that invalidation with 2.7870 mean, Incomprehensibility with 3.2630 mean, Guilt with 3.1764 mean, Simplistic View of Emotion with 2.8805 mean, Devalued with 2.7593 mean, Loss of Control with 2.9439 mean, Numbness with 3.3126 mean, Overly Rational with 2.9443 mean, Duration with 2.8427 mean, Low Consensus with 3.1703 mean, Non-Acceptance of Feelings with 3.0626 mean, Rumination with 3.3947 mean, Low Expression with 2.4732 mean, and Blame with 4.5386 mean are reported [7-9].
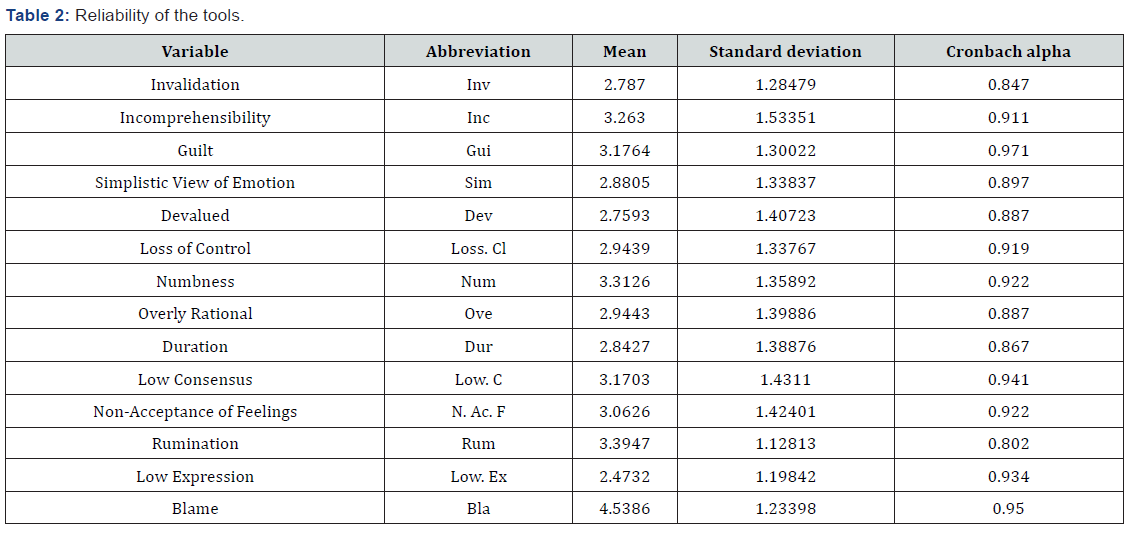
Studying reliability of tools
To study reliability of tools Cronbach alpha was used. Statistic values for variables are as follow: for invalidation is 0.847, for Incomprehensibility is 0.911, for Guilt is 0.971, for Simplistic View of Emotion is 0.897, for Devalued is 0.887, for Loss of Control is 0.919, for Numbness is 0.922, for Overly Rational is 0.887, for Duration is 0.867, for Low Consensus is 0.941, for Non- Acceptance of Feelings is 0.922, for Rumination is 0.802, for Low Expression is 0.934 and for Blame is 0.950. Results of the study indicated that tools are reliable because Cronbach alpha is bigger than 0/7 (Table 2).
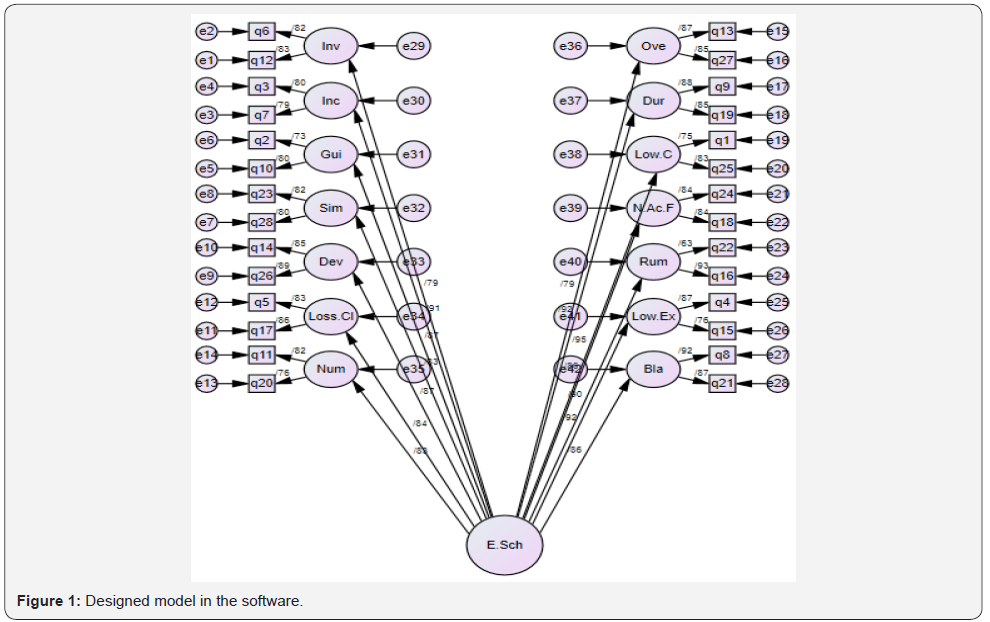
To approve validity, structural equation approach was used by AMOS software. First, for investigating validity of the structure, first and second order Confirmatory Factor Analysis were used. Finally, for studying final model fitting, model fit indices were used. The model is as Figure 1. In this model, 15 latent variables are observed, explained and measure by 28 variables. Results of Confirmatory Factor Analysis in Table 3 are reported [10-12].
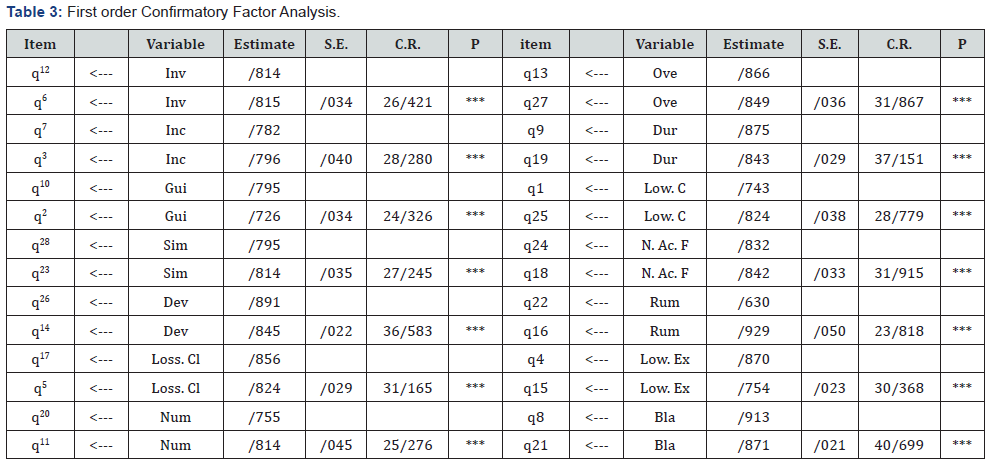
Since CR rate is higher than 1/96 and considering that level of significance is lower than 0/05, all questionnaire items explain and measure significantly their latent variables. Results of second order Confirmatory Factor Analysis are in (Table 4).
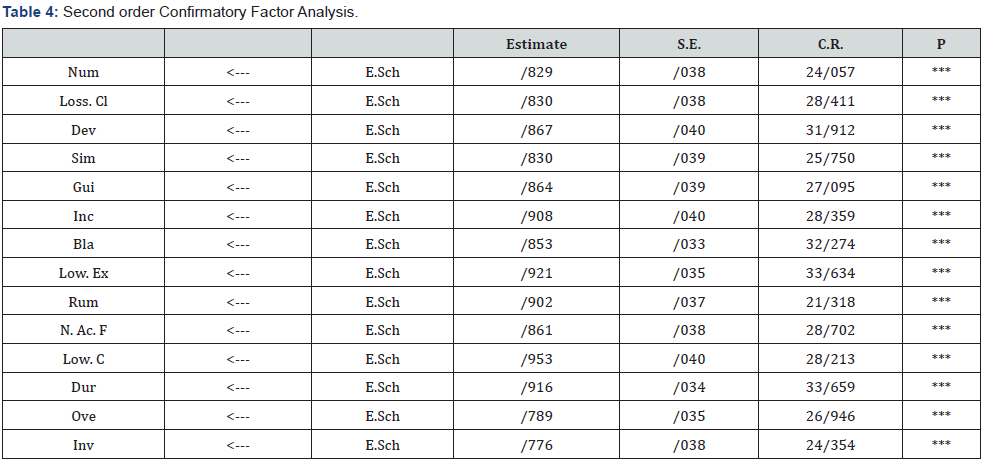
Since CR rate is higher than 1/96 and considering that level of significance is lower than 0/05, all 14 variables under study explain and measure significantly E.Sch as latent variables. Factor load for Invalidation is 0.776, for Incomprehensibility is 0.908, for Guilt is 0.864, for Loss of Control is 0.830, for Numbness is 0.829, for Overly Rational is 0.789, for Duration is 0.916, for Low Consensus is0.953, for Non-Acceptance of Feelings is0.861, for Rumination is 0.902, for Low Expression is 0.921 and for blame is 0.853. Results of model fit are reported in (Table 5).
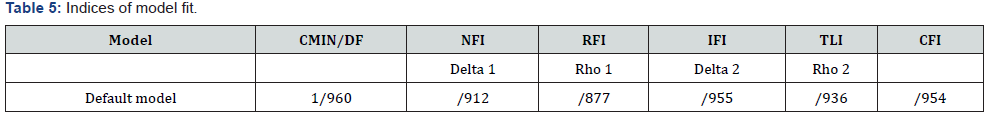
The relative chi-square divided by the degrees of freedom is good standard for the model and supporting data. Criterion for acceptance of this index ranges from 1to 5 which values near to 2 to 3 are explained as best values. Schumacker & Lomax defined 1-5 values for fit index while Mclv, & Carmines believed values in 2-3 range are acceptable. Owlman in 2001 accepted 1-2 range as good value and [7] assumed 1-3 as acceptable variables.
In above table, 960/1 is reported as Chi square which can be considered as acceptable variable. NFI value or normed fit index of Bentler and Bount was obtained 0/912 which is considered as good value based on 0/9 standard value. Therefore, this model is approved, and it is fit. RFI value of relative fit index is 0/877 which is considered as relative fit according to 0/90 as standard value. IFI value or incremental fit index is 0/955 which approves goodness of fit. TLI value of talkler- Louis was 0/936 which considering 0/90 as standard fit approved goodness of fit. CFI value or comparative fit index is 0/954 which is good fit considering standard value of 0/90 [13-16].
Discussion
The results of this study show that the Ukrainian version of LESS is a reliable and valid scale for the assessment of beliefs and attributions about emotions on non-clinical population. People towards their emotions. High level of reliability of Ukrainian version indicates that aim of the scale is appropriate. The relative chi-square divided by the degrees of freedom is good standard for the model and supporting data. Criterion for acceptance of this index ranges from 1to 5 which values near to 2 to 3 are explained as best values [17]. Schumacker & Lomax defined 1-5 values for fit index while Mclv, & Carmines believed values in 2-3 range are acceptable. Owlman in 2001 accepted 1-2 range as good value and [7] assumed 1-3 as acceptable variables. In above table, 960/1 is reported as Chi square which can be considered as acceptable variable.
Conclusion
NFI value or normed fit index of Bentler and Bount was obtained 0/912 which is considered as good value based on 0/9 standard value. Therefore, this model is approved, and it is fit. RFI value of relative fit index is 0/877 which is considered as relative fit according to 0/90 as standard value. IFI value or incremental fit index is 0/955 which approves goodness of fit [18]. TLI value of talker-Louis was 0/936 which considering 0/90 as standard fit approved goodness of fit. CFI value or comparative fit index is 0/954 which is good fit considering standard value of 0/90. The results of the study showed that due to the Cronbach’s alpha that is higher than 0.7, the reliability of all variables is desirable. Confirmatory factor analyses support the schema domains. We conclude that the LessII is a psychometrically sound instrument that can be used Ukraine in research on early maladaptive schemas. Further research is necessary particularly in larger clinical samples.



No comments:
Post a Comment