Global Journal of Nanomedicine - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
Leishmaniasis known as Kala azar in India is transmitted by the protozoan parasite phlebotomine sandfly. There are more than 20 parasites species found in the world. Since many millions are affected and thousands of deaths occur every year this is a neglected tropical disease. There are more than 90 countries affected which contain developed countries and developing countries. The countries include the Eastern Mediterranean region, South Asian countries, Africa and South America. The WHO is taking preventive measures to eradicate this disease within 2020. There are three forms of leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis (VL) which affects the liver and spleen, muco-cutaneous leishmaniasis which affects the oral cavity and nasal tract and cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) which affects the skin. The current treatment available for the disease is pentavalent antimony compounds such as sodium stibogluconate, macrolide compound amphotericin B and Alkylphosphocholine miltefosine. In these drugs severe side effects and toxicity is observed. So, the current strategy available for these drugs is treatment through nanomedicine. Nanotechnology has emerged as an alternative drug delivered by nanocarriers with improved bioavailability and reduced side effects, together with other characteristics that help to reduce the toxicity. Nanotechnology has shown enormous growth in recent years in the application of new drug delivery devices to antileishmanial drug to the targeted cells, tissues and organs specifically with minimizing the toxic effects to normal cells. This review attempts to present a comprehensive overview of different nanocarriers that have greatly contributed to improving the efficacy of anti-leishmaniasis drugs].
Keywords: Nanotechnology; Leishmaniasis; Liposomes; Niosomes; Nanoparticles
Introduction
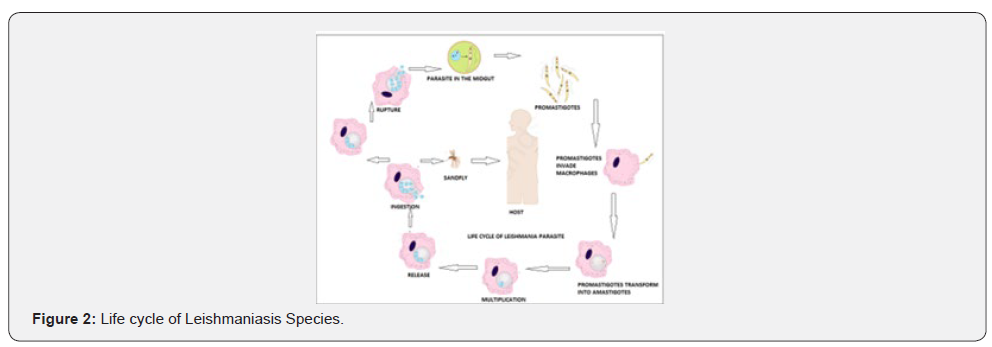
Leishmaniasis is a vector borne disease transmitted by sand flies. Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease caused by more than 20 Leishmania protozoan parasite specie [1]. Almost 2.5 million people are affected all over the world, 1 -1.5 million are affected by cutaneous Leishmaniasis and in India over 90000 are affected by visceral Leishmaniasis [2]. From 2004–2008 there were an estimated 200,000–400,000 cases and 20,000–40,000 deaths per year globally [3]. The current perspective of the disease is that WHO is trying to eradicate the disease within 2020. WHO is taking preventive measures to eradicate the disease and the parasite vector in spraying of pesticides, protection and prevention against the vectors? The environmental and climatic condition is suitable for the insect vector to grow. It is also found in epidemic and non endemic areas of the country. The main cause of the disease is poor sanitary conditions for the vector to grow using animals as host and this disease is carried over to humans through a bite of the insect.
There are three main types of leishmaniasis: Cutaneous, visceral and mucocutaneous. Since the symptom of the disease are severe with skin lesions which do not disappear for lifetime in cutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis where liver and spleen and lymph nodes gets damaged and leads to death and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis leads to loss of oral cavity and nasal tract. The first-line drugs for treatment of leishmaniasis include pentavalent antimony compounds such as stibogluconate [4]. The drugs have severe toxic side effects, such as cardiotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. The parasite has developed resistance to this drug. The second-line drugs for treatment of leishmaniasis include macrolide compound amphotericin B [5]. The severe side effects include nephrotoxicity and cardiotoxicity and it is very expensive. Alkylphosphocholine miltefosine was the first approved orally administered antileishmanial drug on the market. The main side effects being related to toxicity to the gastrointestinal tract. Due to teratogenic effects of miltefosine, it is not used for treatment in pregnant women [6].
Nanoparticles are materials with sizes in the range of 1-100 nm. Nanostructured materials can reach the targeted site like liver, spleen and bone marrow. Nanotechnology is gaining importance day by day the drug is administered into the cells, tissues and organs directly. Some drawbacks are seen in tablet formulations, emulsions and suspension, the drug does not reach the site and the drug is not administered completely to the targeted site of application. Many diseases like cancer, neurological disorders, vector borne diseases like malaria, filariasis, Leishmaniasis. The drug can be administered to the active site with complete bioavailability through nanoparticles. The isolated compound can be incorporated in the nanoparticle and delivered to the desired site of action through Nanotechnology (Figures 1-3). There are number of methods employed in nanotechnology. In this review we have added few important uses, advantages and significance of nanoparticles.
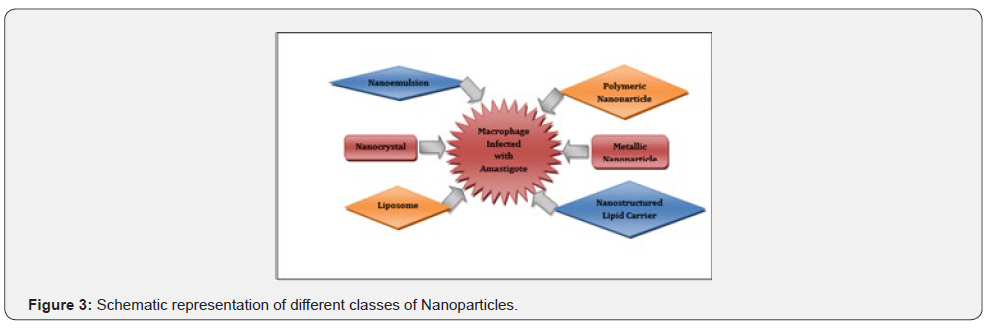
Liposomes
Liposomes are small minute vesicles which are spherical in shape that can be prepared from cholesterol and phospholipids. They are compatible due to their minute particle size, solubility, stability and dissolutions. Liposomes are currently used as DDS for the treatment of different diseases. Most liposomal formulations available in the market target many diseases like cancer and neurological disorders [7].
Nano emulsions and Niosomes
They are mixtures of two immiscible liquids their stability can be enhanced by adding a surfactant (emulsifier). The surfactants are added in these preparations to decreases the interfacial tension and for the creation of small droplets. The emulsifier also plays a significant role in increasing the stability of NE [8].
Solid lipid Nanoparticles
They are prepared from phospholipids, Tweens, polyoxyethylene ethers, and polyvinyl alcohol. The lipids used in their production are stable at room temperature and they have very good potency, high efficacy and low toxicity and side effects [9].
Polymer Nanoparticles
Polymer based nanoparticles may be used in treating infectious diseases such as leishmaniasis, cancer, neurological and vector borne diseases. Since their small size enables them to pass through plasma membrane and biological barriers upon parenteral administration, also enhancing absorption and enabling therapeutic agents to be delivered to infected cells, tissues and organs [10]. Polymer nanoparticles have certain advantages, such as increased bioavailability, compatibility, biodegradability, and release of the encapsulated drug to the targeted site of action.
Biodegradable Nanoparticles
They can be prepared from a variety of materials such as proteins, polysaccharides and synthetic biodegradable polymers. Advantages [11].
i. Desired particle size of the nanoformulation,
ii. Varied properties of the drug i.e. solubility and stability,
iii. Surface characteristics,
iv. Biodegradability and compatibility,
v. Drug delivery profile of the finished product.
Poly-D-L- lactide-co-glycolide
Poly-D-L- lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) is one of the most successfully used biodegradable polymers. It undergoes hydrolysis in the body to produce glycolic acid and lactic acid. Since glycolic acids and lactic acid are naturally found in the body and participate in a number of biosynthetic pathways, there is very minimum side effects and toxicity with the use of PLGA for the targeted drug delivery [12,13].
Metallic Nanoparticles
Metallic nanoparticles such as gold and silver nanoparticles are now receiving considerable attention in the pharmaceutical field. They exhibit several important facts and different functions i.e., diagnostic and therapeutic efficacy to be combined in a single dosage form [14,15].
Nanocrystals
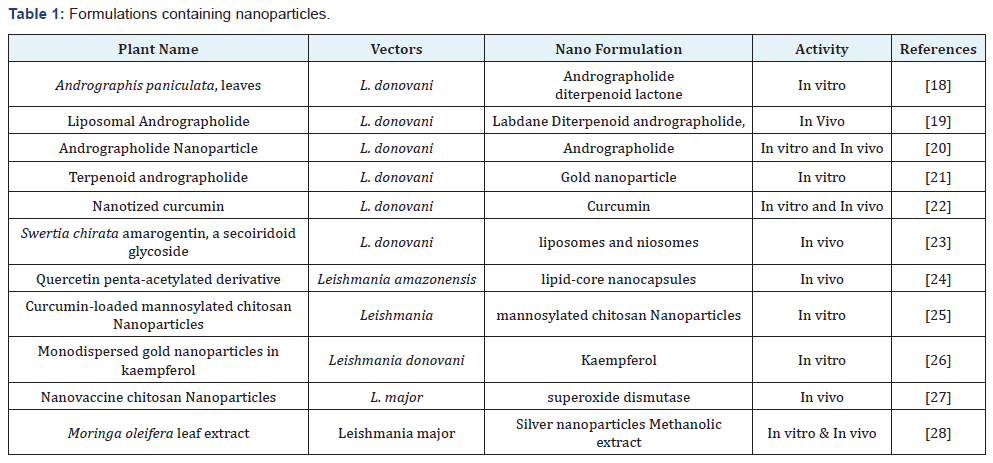
Nanocrystals are pure solid drug particles, particle size in range of 1000 nm. They are usually stabilized by using a polysmeric stearic stabilizers or surfactants. They are 100% drug without any carrier’s molecule attached to it [16,17]. The different dosage forms and formulations available in the form of nanoparticles, liposomes, neosomes etc. are reported in this study (Table 1).
Conclusion
The present review focuses on the recent advances in nanotechnology. Initially, the use of nanotechnology was largely based on enhancing the stability, absorption, biodegradability, biocompatibility, bioavailability, dissolution and controlled release of drugs [18-28]. Hence enhancing the efficacy and potency of known natural bioactive compounds through nanotechnology has become a feature trend. The efficacy of these natural products has greatly improved through the use of nanocarriers formulated with metallic nanoparticles like, gold & silver nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles together with solid lipid nanoparticles, nanocrystal, liposomes, niosomes, nanoemulsions, biodegradable nanoparticles and lipid core nano capsules, etc. There has been a continued demand for novel natural biomaterials for their quality of being biodegradable, biocompatible, availability, renewable resources, less side effects and low toxicity. Nanotechnology being applied to treat leishmaniasis is a relatively new area of research and still needs to be enhanced with the available data that will arise when nanotechnology will be applied to various aspects to treat leishmanial disease.
To Know more about Global Journal of Nanomedicine
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/gjn/index.php
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php



No comments:
Post a Comment