Annals of Reviews and Research - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
The article is dedicated to the analysis of the hydrogeological process’s formation condition in the Baku city zone and evaluation of the subsoil waters suitability for verdures irrigation. It was determined that a quality of the subsoil waters is suitable for the verdure irrigation in the central, eastern and western parts of the zone, but it is unfit in the northern, north-eastern and south-western parts - local areas of the region. The regionalization of the subsoil waters according to the suitableness degree for irrigation was performed in the Baku city and “A map of the schematic regionalization according to the suitableness degree of the subsoil waters the verdures irrigation in the Baku city” was compiled.
Keywords: Hydrogeological condition; Geological system; Regime; Underground water; Urbanization; Stratigraphic floors; Mineralization; Rocks
Introduction
Lately, a special attention is paid to the renovation and greenery measures realization in Baku and Absheron. That’s why a large usage of the available water-collecting and new water-collecting construction are intended in Baku. An investigation of the hydrogeological process formation legitimaies, research of the watery horizons waterness and various aims, including an evaluation of the subsoil waters quality for verdures watering are a problem actuality. The underground hydrosphere in Baku was adopted as a research object. An aim of the research consists of hydrogeological processes formation condition analysis and an evaluation of the subsoil waters fitness for the verdures watering. The complex research method was used: the materials analysis on geomorphological, tectonic, geological structure and natural condition which set a subsoil water regime; hydrodynamic and hydro chemical methods determining a condition of the hydrogeological processes formation; theoretic methods for a quality assessment of the subsoil waters quality with the purpose of irrigation. There is a great practical importance of the problem that finds its solution in the article. So, definition of the subsoil waters regime forming condition permits to evaluate a modern hydrogeological condition, but the subsoil waters quality assessment gives a chance to fix these waters-use directions.
Analysis and Discussion
An area of the Absheron peninsula is 2000 km2, it is situated in the eastern part of the Azerbaijan Republic. The peninsula was surrounded by the Caspian Sea in the north, east and southern parts, but by the Gobustan foothill plain from west. Gardening and orcharding developed, besides being the largest center of the oil-gas refining and extracting enterprises here. The main living places are Baku, Sum-gait, Khirdalan, Shuvalan, Lokbatan, Sahil, Alat and others. The living points commu-nicate with each over by electricity, railways and automobile roads. Baku a capital of the republic is situated in the Baku bay coast which is one of the natural gulfs in the Caspian Sea. Baku is port city with the international and sandy beaches. It is possible to go aboard ship to the Atlantic and Arctic oceans from here. The sunny shores and sandy beaches are a great importance as a health resort, tourism and rest zone. Azerbaijan is famous with its oil and gas deposits since ancient.
The oil and gas deposits are in the Absheron peninsula, zone of the Caspian Sea, Baku and Absheron archipelagos. The Jeyranbatan reservoir plays a great role in water-supply of the industrial enterprises and population in the Absheron peninsula and irrigation of the sowing areas in the Absheron gardens. Its area is nealy 14 km2. The water-source is provided by the Samur-Absheron canal. The subsoil waters in the Baku city spread in all the stratigraphic stage deposits. The subsoil water flow possesses a single circular flow in the sea direction [1]. Presence of Balakhani-Sabunchu-Ramani, Surakhani and Garachukhur-Zig anti-clinals in the eastern part of the city makes a condition for the subsoil water flow form change. The subsoil waters flow spreads in all the directions of these structures as a circular form. The hydro relief inclination is changeable in the city zone. The inclination changes by 0,01-0,1 in the west and east; 0,06-0,01 in the north; 0,014-0,1 in the south. It changes by 0,003-0,08 in Keshla [2].
Some natural and artificial factors participate in the subsoil waters formation in Baku.
The geological-geomorphological factors from the natural ones are considered important in formation and circulation of the subsoil waters. The deposits of the fourth period spread widely in Baku and they are investigated in the different depths. Having a high water-conductivity of these deposits is a great importance in formation of the subsoil waters-supply. So, a water-penetrating coefficient of the water-holding rocks changes by 0,1-25,9m/day [3]. It is known that the zone relief has an important role in creation of the subsoil waters. From this point of view, the ravines, hollows and holds make a good condition for the subsoil waters collection, such relief forms spread widely in Baku. There are stone-quarries of the anthropogenic, old stone, clay and limestones, besides the natural relief forms in the Baku amphitheatre surface, they are filled with water flows: subsoil waters or industrial waste waters in many places. Such quarries are mainly observed in the Alatava area. There are large ancient and modern ravines in the Baku city zone, one of them is in the Yasamal valley consisting of undeveloped and gorges, valleys, the other is strong developed Bibi-Heybat ravine in Patamdar settlement.
The researches show that many parts of the yearly rainfall quantity fall in the autumn-winter period, and this displays itself with the gravitation moisture presence in the aeration zones of the ditches, ravines and other areas with the good micro-relief. The climate factors determine quantity and quality indications of the subsoil waters creating to an important degree. 227 m (on average) atmospheric precipitations, 947-1344 mm evaporation is observed in the zone for a year. An average yearly mineralization degree of the atmospheric precipitations is 102 mg/l. 184,8 kg/hectare salt enter the land surface a year (12,9% of it is NaCl). The water evaporations condensation role isn’t little in the subsoil waters formation. As is known, the condensation waters feed the subsoil waters in the places with the good condition for the water evaporation condensation (in the places with the air’s high relative humidity, little bed depth of subsoil waters, the air temperature change in the large diapason). There is abovementioned suitable condition for the water evaporations condensation in the Baku city.
The research show that the condensation happens over all the density of the aeration zone and subsoil water surface from October to April. The highest value of condensation is observed in the sand, but the less value is in the clay. While rising salinity of the soils and subsoil waters, including humidity shortage, the condensation process intensity gets increased, too. The hydrological factors influence the underground waters discharge. However, a base of this process is the Caspian Sea’s level change (falling and rising). Since 1978 the subsoil waters level has risen 0,4 -1,3m as a result of the sea level rising constantly (2,5m) (according to the hydrogeological observations results per-formed in the regime-observation net). The sea level rising damaged the Republic economy. So, the oilfields, oilwells, pump stations remained under water. All the objects, dwelling and administrative houses’ cellars exposed to the flooding process in connection with the water level rising in the Caspian Sea. An impact of the subsoil waters on feeding of some salty lakes spreading in the peninsula and Baku city isn’t little.
It should be noted that Baku city and Absheron peninsula concern the arid climatic zone, the quick development of the desertification process caused superiority of the artificial factors impact in subsoil waters feeding at present, while the underground waters regime is formed under the climate factors influence [4]. The water from the artificial factors and infiltration from the waters used for the verdures watering possess an important role in subsoil waters feeding. An analysis of the balance table of the subsoil waters in Baku permits to come to such a conclusion that a main role in subsoil waters feeding belongs to the artificial factors. So, 91,4% of the income part from the subsoil water balance is connected with the artificial factors (filtering from 63,2% - water nets; flow from 23,5% - sewerage waters; infiltration from atmospheric irrigative waters); 8,6% is connected with the natural factors (infiltration from atmospheric precipitations and feeding at the expense of condensation waters).
We should note that the rocks of the subsoil water horizon are very watery. During the water-drawing the wells expenditure was registered by 0,2-5,9l/s. The highest waterness is observed in Yasamal. Its reason is explained by the Ganli Lake impact. A special expenditure of the wells is 0,02-0,3l/s∙m. The wells expenditure in the central parts of the city is 0,2-5,0l/s, a special expenditure 0,02-0,3l/s∙m [5]. It was determined that a mineralization degree of the subsoil waters is 1-2g/l in the central part of Baku. Exception the city, west border, all the foreign borders are surrounded by the subsoil waters with 10-20g/l and more mineralization. This is related to the Boyukshor Lake effect. A chemical composition of the waters is Cl-Na, Cl-SO4-Na-Mg, SO4-HCO3-Cl-Na-Ca-Mg. Exception this compostion, all the possible combinations of ions are found. The subsoil waters with the weak mineralization surround a great area of Baku [6].
The area which is surrounded by the verdures in the city zone is 3500 hectares. An ancient primary plant cover:Eldar-pine, olive, plane, fig, apple, quince, cherry, mulberry trees.
The experiment shows that a quality of the irrigated waters for the verdures watering depends on their turbidity, mineralization degree, chemical composition and temperature. So, a temperature of the irrigated waters must be 15-300C; pH index-6,5-8,0; mineralization degree - 1,0-1,5g/l. While a mineralization degree is more than the presented norm the irrigation process should be fulfilled with the measure which prevents a danger of the soil’s salinity (for ex. gypsum must be given into the soil). We should note that exception a mineralization degree of the irrigated waters, their chemical composition must be absolutely taken into account. So, the most harmful salts in the irrigated waters composition are considered soda (Na2CO3), NaCl and Na2SO4. A quantity of these salts in the soils having a good water con-ductivity shouldn’t pass over the following limit: soda (Na2CO3)<0,1%; NaCl<0,2%; Na2SO4<0,5% [7]. At the same time the soil solonetz negatively influences the verdures develop-ment. So, hardening of the place which in the plant root is situated in the solonets soils and structure disorder limit the soils fertility, and this is a reason for the plant perishing.
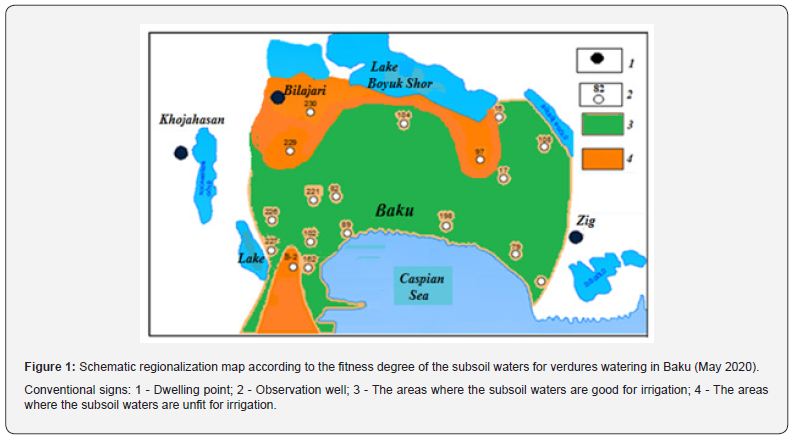
The experiment displays that Na ion absorbed by the soil is mainly a reason for the hardened soil layer formation. The soil has an absorbing and holding ability of various substances which are in contact with the soil (gas, salt, cation and anions). But the absorbed ions aren’t washed by the water, they are kept in the soil. The soil possessing an absorbing ability can absorb Ca, Mg, Na and H ions to a Definity quantity from the soil solution and can be changed with each other to an equivalent number. Taking into account a natural condition good for the soils salinization and solonetzification, i.e. concerning the Baku city zone the arid climate, the irrigated waters quality was evaluated by the zone definition method of the Na-n relative potential adsorption and it was defined that the subsoil waters are fit for irrigation in the central, eastern and western parts of the zone. So, usage of the subsoil waters in the presented areas for irrigation doesn’t create a danger for the soil salinization and solonetzification. Unfitness of the subsoil waters quality in the local areas for irrigation has been investigated in the northern, north-eastern and south-western parts (the soil salinezation and solonetzification is inevitable). So, regionalization was performed according to fitness degree of the subsoil waters for irrigation in the Baku zone and “Schematic regionalization map according to the fitness degree of the subsoil waters for verdures watering in the Baku city” was compiled (Figure 1).
Conclusion
The natural and artificial factors participate in subsoil waters feeding in Baku and a main role belongs to the artificial factors at present while occurring the subsoil waters feeding at the expense of the natural factors for long years. The subsoil waters can be used for watering of the gardens, verdures in the city in future. A quality of the subsoil waters is unfit for irrigation only in the local areas.
To Know more about Annals of Reviews and Research
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php




No comments:
Post a Comment