Robotics & Automation Engineering Journal - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
The temptation to utilize the well-known biometric identification tools in the new digital economic systems is very high. And such practice should be banned. The given report scrutinizes the peculiarities of forensic identification, reveals the impossibility of using traditional parameters in the digital economic systems and offers a new approach, an interactive reflex-based identification, which ensures the trusted identification using untrusted devices.
Keywords: Identification; Biometry; Digital economy; Identification parameters; Identification hypothesis
Introduction
Until recently all studies in the field of the technical information protection have been carried out taking into account the fact that we deal with the corporate systems, whose boundaries are known precisely. Within these boundaries a sufficient level of security can always be ensured, based on the use of the trusted computer aids included in the system. As far as the open systems are concerned, it is simply impossible to raise the issue of assuring the trustedness of all computer aids in this regard. Thus, under no circumstances the users’ mobile access tools can be made trusted. When individuals apply for public services, telemedicine consultations, use banking services or services in the B2C sector, they always use smartphones, the trustedness of which is out of question. Such access will always be easy prey for all types of malware attacks.
Identification methods for corporate systems are well known and are based on the use of both technical devices and human biometric parameters. The use of the biometric parameters is the most attractive tool for the open systems, as they are not alienated from a person, and are inherent in each of us. The biometric parameters used for identification, such as fingerprints, retina and iris, DNA, voice and others, were originally intended for the use in the criminal science. But is there a chance to apply the same biometry that is used in criminalistics to the digital economy systems?
Difference between Identification Tasks in Criminalistics and the Digital Economy
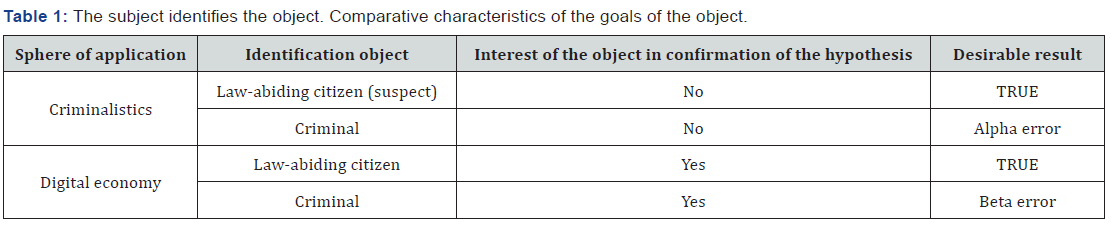
A null identification hypothesis can be formulated by the subject as follows: “An identifiable object is the one he/she pretends to be (the one the subject takes it for).” As a rule, criminalistics deals with people who are not willing to cooperate. Its usual object is a corpse, a suspect or a criminal. The purpose of the analysis is to prove the fact of the committed access of the object - to the weapon and/or crime scene, identification of the victim and so on. And, by all means, the object is usually not interested in correct identification at all. In this regard, the active counteraction on the part of the object is either absent, or is aimed at violation of identification, that is to prove that he/she was not there, wasn’t involved, didn’t break any law.
The technical tools used in this regard are trusted. They are specially developed, protected by certified means, undergo regulatory control procedures and the like. The purpose of counteraction (inaction) is to reject the null hypothesis while it is correct. The counteraction (on the part of the subject, or accomplices, or the difficulties linked with the lack of data) is aimed at achieving the “false positive” error. In the digital economy the identification object is a rather active and law-abiding participant in economic activities. An example of his or her needs is to gain access to some resources. He/she is willing to cooperate and is ready to perform some actions in order to obtain the services he/she needs after successful identification. He/she is interested in correct identification.
The active counteraction to the system can be carried out by a hacker (or simply a malicious person), seeking false identification in his/her favor. The technical means are arbitrary. These are ordinary pads and smartphones, not protected against malware. The purpose of counteraction is to pretend to be somebody else. To force the subject to accept a null hypothesis while it is false. The counteraction (on the part of the hackers) is aimed at achieving the “false negative” error. For illustrative purposes the characteristics and positions of the object of the identification process are summarized in a table (Table 1) below. Degenerated cases (a corpse) are not taken for consideration.
Here we can observe completely opposite characteristics. The differences between positions of the identification subject are no less obvious (Table 2).
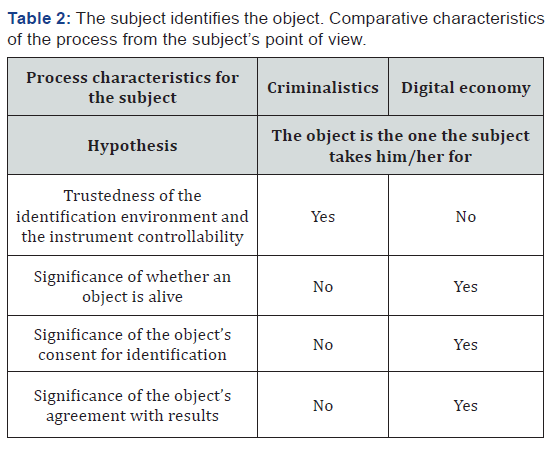
Thus, the identification processes in criminalistics and the digital economy are completely different under the given hypothesis. Given such a profound difference between the processes, the use of the same instruments seems rather strange. It is worth noting that the tool itself only processes the data, it does not generate them. And it is necessary to choose the data that contain the information depending on a particular purpose. In our case, there is a need to consider the peculiarities of the identification features-whether they have enough information for the solution of the set tasks. It is worth noting that due to their simplicity and the static character, the applied modalities (fingerprint, iris and retina, vascular bed, etc.) can be reproduced and modeled easily, which not only enhances the risk of erroneous identification, but also permits to influence its results directly. Traditional (invariant) biometric modalities do not and cannot ensure a sufficient level of the identification trustedness on an untrusted device.
Thus:
1. static biometric characteristics are used in criminalistics for identification and authentication by virtue of their complete or partial invariance to external factors.
2. studies of the application of biometric mechanisms are explicitly or implicitly based on the assumption on the trustedness of the technical processing means.
In our case (the digital economy) this assumption is obviously wrong, and this is a reason why it is necessary to change the approach to biometric characteristics as invariants.
New Biometry
To address the vulnerabilities associated with the simplicity of substitution of measurements on untrusted devices, it is necessary to shift from the static indicators to the dynamic “stimulus - response” type ones, which have a complex dynamics of communication. The human nervous and autonomic nervous systems and related peculiarities of physiological movements are a dynamic link, which is extremely difficult for modeling today. In particular, involuntary reactions to external stimuli (in particular, audio and video stimuli) are individual. The response to stimuli can be recorded by the sensors of the client’s device, processed using artificial intelligence methods, such as artificial neural networks, which will allow to determine the source of the data flows and to improve the authenticity of identification. Based on the capabilities of the modern technical devices (smartphones), such dynamic biometric characteristics of a person as the characteristics of a pulse wave, dynamics of the eyeball change and dynamics of following the stimulus on the screen with an eye can be recorded reliably. In order to do this, it is sufficient to have a camera and a flash (flashlight), as well as a touch screen in the smartphone.
The study of the eye movements is a promising area. It is sufficient to note that the movements of the eyes are controlled by 7 muscles (!), and the muscles responsible for the saccadic movements are the fastest ones. Study of the reflex component of the saccades, as well as (and perhaps, primarily) the processes of fixation and regression during reading have a good potential.
Conclusion
Human responses to external stimuli depend considerably on cognitive and kinesiological characteristics of the person, have a dynamic character and are reflected in measurements with a sufficient degree for analysis
The principal peculiarities of the proposed stimulusresponse system are as follows:
1) Availability of the human nervous system as a link between the stimulus and the response.
2) Incidental, non-recurring stimuli.
3) The stimulus-response pair can be processed on a remote trusted device.
In this case:
a. The untrusted client terminal does not affect the results, as the generation of a stimulus and analysis of a response are carried out by means of the alienated trusted resources, and the distortion of the response will not allow the intruder to get the desired result.
b. There is no sense to intercept the stimulus, because knowing the stimulus, it is impossible to generate a response due to the lack of a model of a person.
c. It is impossible to extract parameters of the neural network by testing it.
d. Identification acts specify the parameters of the neural network, and therefore even the comprehensive surveillance will not allow to fully reproduce the network.
To Know more about Robotics & Automation Engineering Journal
Click here: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php





No comments:
Post a Comment