Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences - Juniper Publishers
Abstract
Aim: A simple, accurate, precise, cost effective, rapid and sensitive UV/visible spectrophotometric method was developed for the determination of Saxagliptin in active pharmaceutical dosage form. The developed method was validated as per ICH guidelines. Method: The purity of saxagliptin was characterized by solubility profile, melting point, Fourier Transform Infra-Red. The drug was analyzed using UV/visible spectrophotometric method was validated in terms of linearity, accuracy, precision, specificity, Limit of detection and Limit of quantitation. The solvent used was methanol: water (15:85, v/v) and the wavelength corresponding to maximum absorbance of the drug were found at 204 nm. Result: Melting point of drug was found 101°C nearly corresponds to its actual melting range. The linear response for concentration range of 2-10 μg/ml of saxagliptin was recorded with y = 0.1126x - 0.0103, regression coefficient r2 = 0.99068. The accuracy was found between 93.75- 104.16%. Precision for intra-day and inter-day was found to be within the limits. To establish the sensitivity of the method, limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were determined which were found to be 6.77 μg /mL and 20.33 μg /mL respectively. Conclusion: The drug was confirmed by interpretation of UV spectra. Hence proposed method stands out validated and thus may be used for routine analysis of Saxagliptin in pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Keywords: Spectrophotometric method; Saxagliptin; Methanol; Water; Melting point
Abbreviations: UV spectroscopy: Ultraviolet Spectroscopy; ICH: International Conference on Harmonisation; DPP: Dipeptidyl Peptidase; FTIR: Fourier Transform Infra-Red; LOD: Limit of Detection; LOQ: Limit of Quantification
Introduction
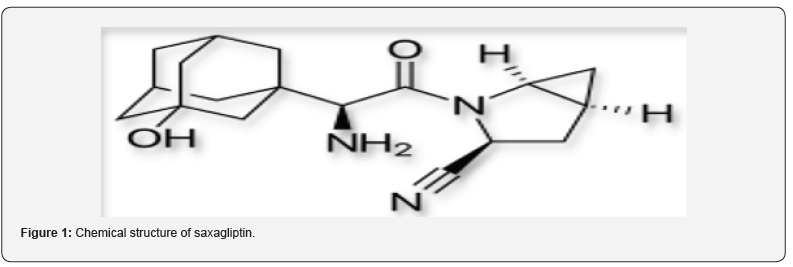
Saxagliptin (SXG) is chemically (1S, 3S, 5S)-2- [(2S)-2-Amino-2-(3 hydroxytricyclo [3.3.1.13,7] dec- 1-yl) acetyl]-2-azabicyclo [3.1.0] hexane-3-carbonitrile previously identified as BMS-477118 as shown in figure 1. The empirical formula is C18H25N3O2.H2O, and the molecular weight is 333.43 [1-4]. Saxagliptin is an oral hypoglycemic or anti-diabetic drug of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DDP-4) inhibitor class. The inhibition of DPP-4 increases levels active of glucagon like peptide 1 (GLP-1), which inhibits glucagon production from pancreatic alpha cells and increases production of insulin from pancreatic beta cells. In 2009, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved saxagliptin and sold under the brand name Onglyza. In adults with type-2 diabetes mellitus, saxagliptin is suggested as an add-on to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control [5-11].
Literature survey reveals that the drug can be estimated only by LC-MS/MS, spectrophotometric method have been reported [12,13]. The aim of the present work was to develop a simple, sensitive, precise and accurate UV/Visible spectrophotometric method for the determination of saxagliptin in its pure form and pharmaceutical formulations further, to validate the developed method.
Materials and Methods
Chemical and reagents
All the chemicals used were of analytical grade. All the solutions were freshly prepared in Methanol and 0.1N HCl (15:85, v/v). Authentic of saxagliptin were obtained as gift samples from Mylan Laboratories Limited, Hyderabad
Methods
Saxagliptin was estimated using UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu model 1800 double beam) at the wavelength of maximum absorption (204 nm) in acidic medium containing 0.1N HCl. The drug was characterized by solubility, melting point, and Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) techniques. The analysis of the drug was carried out by UV-Visible method which was validated analytical parameters like linearity, precision, and accuracy as per guidelines laid down by International Conference on Harmonization (ICH).
Physical characterization of saxagliptin
The physical characterization of procured drug sample of saxagliptin was determined on the basis of following parameters.
Organoleptic properties
The organoleptic properties have been determined for nature, colour, taste and odour of the pure sample of saxagliptin
Solubility
Excess amount of saxagliptin was dissolved in 10 ml distilled water till a saturated solution was obtained. The saturated solution of saxagliptin was stirred for 48 hrs on magnetic stirrer at 100rpm and room temperature (at 25 ± 1ºC). Then the sample was centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 rpm. Clear supernant was collected using 0.22 μm syringe filter and analysed using UV spectrophotometer. The results were analysed and noted [14].
Melting point
Melting point of saxagliptin was determined using capillary melting point apparatus. In this method a small quantity of drug was filled in a capillary tube open both the ends and it was placed along with thermometer in melting point apparatus.
Fourier transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectrum was used as an analytical technique for identification of pure drug sample by KBr method using FTIR spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, USA). Peaks of individual pure drug were compared with reference FTIR peaks. Samples were previously prepared with KBr at 1: 5 (sample: KBr, w/w). KBr disks were prepared by compressing the powders at a pressure of 5 tons for 3 min in a hydraulic press and scanned against a blank KBr disk at wave numbers ranging from 500 to 4000 cm-1 with a resolution of 1.0 cm-1 [15].
Analytical method for drug concentration measurements (UV/Visible method)
The ultraviolet spectrophotometric method was selected for the estimation of saxagliptin in the range of 200 to 400 nm and the λmax was determined.
Diluent preparation
Methanol and 0.1N HCl (15:85, v/v) were used as a diluents.
Preparation of saxagliptin stock solution (20μg/ml) in 0.1N HCl
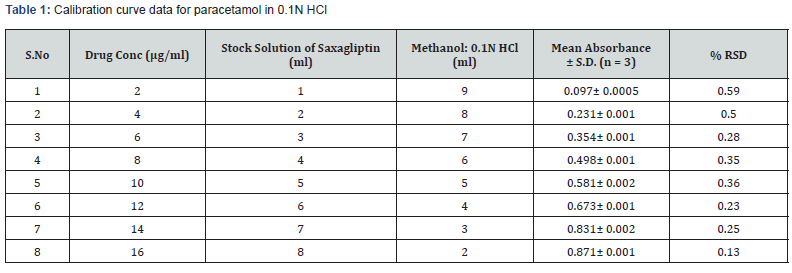
Saxagliptin was weighed equivalent to 100mg and transferred into 100ml volumetric flask then 15ml of methanol was added and shaked well to dissolve it after that the volume was made up to 100ml with 0.1N HCl. From that 2ml of solution was withdrawn and taken in 100ml volumetric flask. The volume was adjusted with diluent up to up to 100ml with 0.1N HCl [16,17] as shown in table 1.
Selection of detection wavelength
Drug solution was scanned over the range of 200- 400 nm. The wavelength of saxagliptin was determined to be 204 nm.
Preparation of working standard
Prepare a series of dilute solution from the above stock solution according to table 2 in 10 ml volumetric flask. Measure the absorbance of the solutions at 204 nm using distilled water as a blank. Plot a graph by taking concentration (μg/ml) on X-axis and absorbance on Y-axis. This plot gives a straight line and the linearity can be determined using y = mx + C formula. From the calibration curve calculate the Coefficient of determination R2 value, slope m and intercept C using the following formula, OR by excel sheet.
Construction of calibration curve
Pipette out 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, and 8 ml of working solution and transfer into separate 10 ml volumetric flasks. Dilute all of them to 10 ml with water to get solution of concentrations to 2, 4, 6,8,10,12,14,16 μg/ml respectively
UV Method Validation
The ultraviolet spectrophotometric method was validated for accuracy, precision, linearity, detection limit, quantitation limit and robustness [18-20].
Linearity
Appropriate aliquots of saxagliptin working standard solutions were taken in different 10 ml volumetric asks and diluted up to the mark with distilled water to obtain final concentrations of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 μg/ml. Calibration curves were constructed by plotting absorbance versus concentrations and regression equations were calculated for both the drugs.
Range
The Range of the analytical method was decided from the interval between the upper and lower level of the calibration curve by plotting curve.
Precision
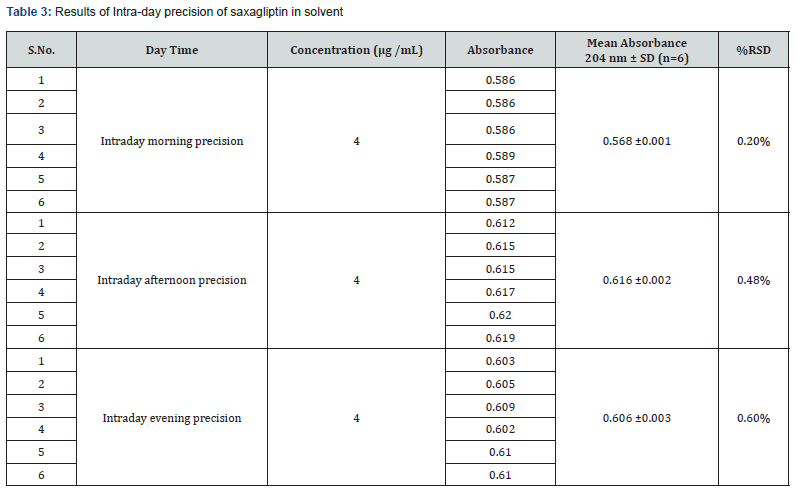
Intraday precision was determined by analyzing the drugs at concentrations (4μg/mL) and each concentration for three times, on the same day. Inter-day precision was determined similarly, but the analysis is carried out daily, for two consecutive days. Repeatability (intraday) of the method was determined by analyzing six samples of the same concentrations of the drug (4μg/mL). The absorbance of each was measured and reported in terms of relative standard deviation to obtain the variation.
Accuracy
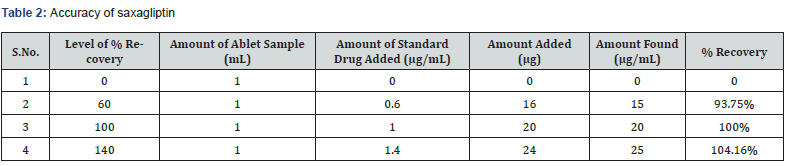
The accuracy of the method was determined by calculating recoveries of saxagliptin by method of standard additions at three different levels 60, 100 and 140 %. Mean percentage recovery was determined. Recovery values were calculated and shown in table 1.
Detection limit
The Detection Limit of an individual analytical procedure is the lowest amount of analyte in a sample which can be detected but not necessarily quantitated as an exact value. The detection limit (LOD) may be expressed as. LOD= 3.3σ/S Where σ = Relative standard deviation of the response. S = the slope of the calibration curve (of the analyte).
Quantitation Limit
The Quantitation limit of an analytical procedure is the lowest amount of analyte in a sample, which can be quantitatively determined with suitable precision and accuracy.
Quantitation Limit (LOQ) may be expressed as: LOQ = 10σ/S Where
σ = Relative standard deviation of the response.
S = the slope of the calibration curve (of the analyte).
Results & Discussion
Organoleptic properties
Saxagliptin was found to be white colored, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility
The solubility of saxagliptin in water was found to be 2.12 ± 0.28 mg/L corresponding to reference value of 2.9 mg/L.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
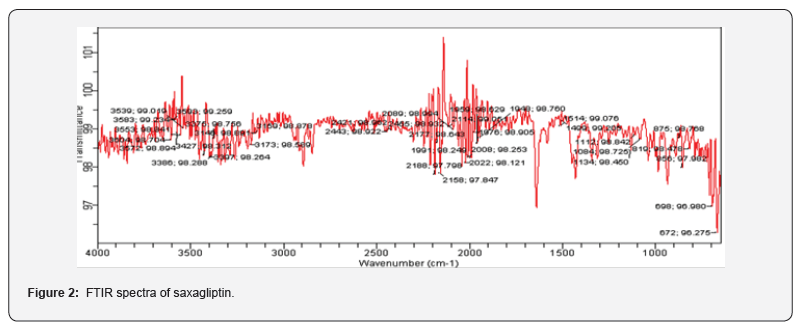
FTIR spectrum for identification of pure drug sample was done by FTIR spectrometer. Major absorption peaks of saxagliptin was found at 3450.12 cm-1 (N-H stretching), 2912.61 cm-1 (C-H stretching), 3301 cm-1 (OH stretching), 1614.47 cm-1 (C-N stretching), 1255.70 cm-1 (C-O stretching) as shown in figure 2 which corresponds to the literature peaks confirming the purity of drug sample.
Melting point
The melting point was determined by capillary melting point apparatus. The observed melting point of saxagliptin is 101°C
Analytical method for drug concentration measurements (UV/VIS Method)
Selection of detection wavelength: The wavelength of saxagliptin was determined to be 204 nm as shown in figure 3.
Preparation of standard plot for saxagliptin: Absorbance of the resultant solution was measured at 204 nm using blank. A graph was plotted between the concentrations and their respective absorbance. The response of the drug was found linear in the entire investigational range of 2 to 10μg/ml as shown in table 1. The calibration curve showed the linear equation as, y = 0.1126x - 0.0103, with a correlation coefficient, r2 = 0.99068, where y represents absorbance (optical density) and x represents the concentration (μg /ml) as shown in figure 4.
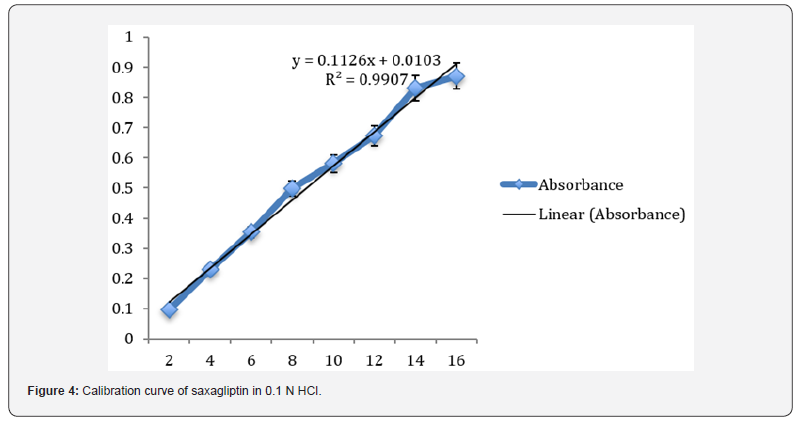
Method validation: The developed method was validated as per ICH guidelines for the following parameters:
Linearity: The linearity for Saxagliptin was found to be linear in the range of 2-10 μg/ml. The regression equation was found to be y = 0.1126x - 0.0103, r2 = 0.99068.
Range: The observed range of saxagliptin in test solution was observed from 0.097± 0.0005 to 0.871± 0.001.
Accuracy: The accuracy of the analytical method for Saxagliptin was determined at 60%, 100% and 140% levels of standard solution. Absorbance was measured at 204 nm and results were expressed in terms of % recoveries in table 2.
Precision: The Intra-day and Inter-day precision were carried out using same optimized conditions. The precision (measurement of inter-day, intra-day repeatability) results showed good reproducibility with the relative standard deviation (% RSD) below 2.0 % as shown in table 3 & 4 respectively. This indicated that the method was highly precise.

Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ): LOD and LOQ of method were determined to be 6.77 μg /mL and 20.33 μg /mL respectively. LOD and LOQ indicate that method was highly sensitive and fast.
Conclusion
The method was validated and found to be simple, sensitive, accurate and precise as per ICH guidelines [21]. The % RSD for the validation parameters was found to be less than 2%. Hence proposed method may be used for routine analysis of these drugs in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Accuracy of proposed method was confirmed by performing accuracy studies that showed the results within the range. Precision of proposed UV method was confirmed by performing intra-day and inter-day precision. Results were well within acceptance criteria that indicate excellent scope of the method for the determination of Saxagliptin in pharmaceutical dosage forms and bulk.




No comments:
Post a Comment